Data Storage Solution in Healthcare: Which is the Best Option

Data storage is always a big concern among healthcare organizations, especially in terms of data storage solution.
While the rapid increase in healthcare data presents numerous opportunities for medical organizations – such as gaining valuable insights, making informed decisions, improving preventive medicine, and providing better patient care – healthcare providers face the challenge of maintaining accurate, up-to-date, and secure medical information.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of proper healthcare data storage and management, introduce the most common data storage solution, discuss industry trends, and offer actionable best practices for healthcare organization leaders.
I. What is Data Storage in Healthcare
Data storage refers to the use of magnetic, optical, or mechanical media to record and preserve digital information for ongoing or future operations. This can be done on physical hard drives, disk drives, USB drives, or virtually in the cloud.
The key is ensuring that files are backed up and readily available in case of system failures. Important factors to consider for data storage include reliability, security features, and the cost of implementing and maintaining the infrastructure.
In healthcare, data storage encompasses patient records, demographics, insurance information, administrative data, and more. Interoperability is crucial for managing health data, as it needs to be shared among various parties during a patient’s care.
Authorized access, exchange, and cooperative use of patient information within a healthcare organization or with external regional or national entities directly affect the efficiency, quality, and safety of patient care.
II. Data Storage Solutions in Healthcare
Healthcare data storage is crucial for effective data management. Organizations may use on-premises, cloud solutions, or a combination of both. Here are common data storage solutions to handle the growing volume of data:
Private Data Storage
Private data storage, also known as on-premises storage, involves storing all of an organization’s data in-house. This includes managing all aspects of data storage, such as server maintenance, physical security, and temperature control. On-premises storage falls into three main categories: direct-attached storage, network-attached storage, and storage area networks.
1. Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
A number of businesses, including healthcare firms, use direct-attached storage (DAS), often without realizing it. For instance, most laptops have a DAS hard drive. DAS involves storage hardware like an external hard drive or USB drive connected directly to a device.
DAS data storage solution is one of the most affordable data storage options. For example, a 5TB external hard drive can be purchased for under $200, making it ideal for small businesses with limited data. But DAS is not very shareable. To share data or access it from another location, you need to either bring the DAS device with you or upload the files online.
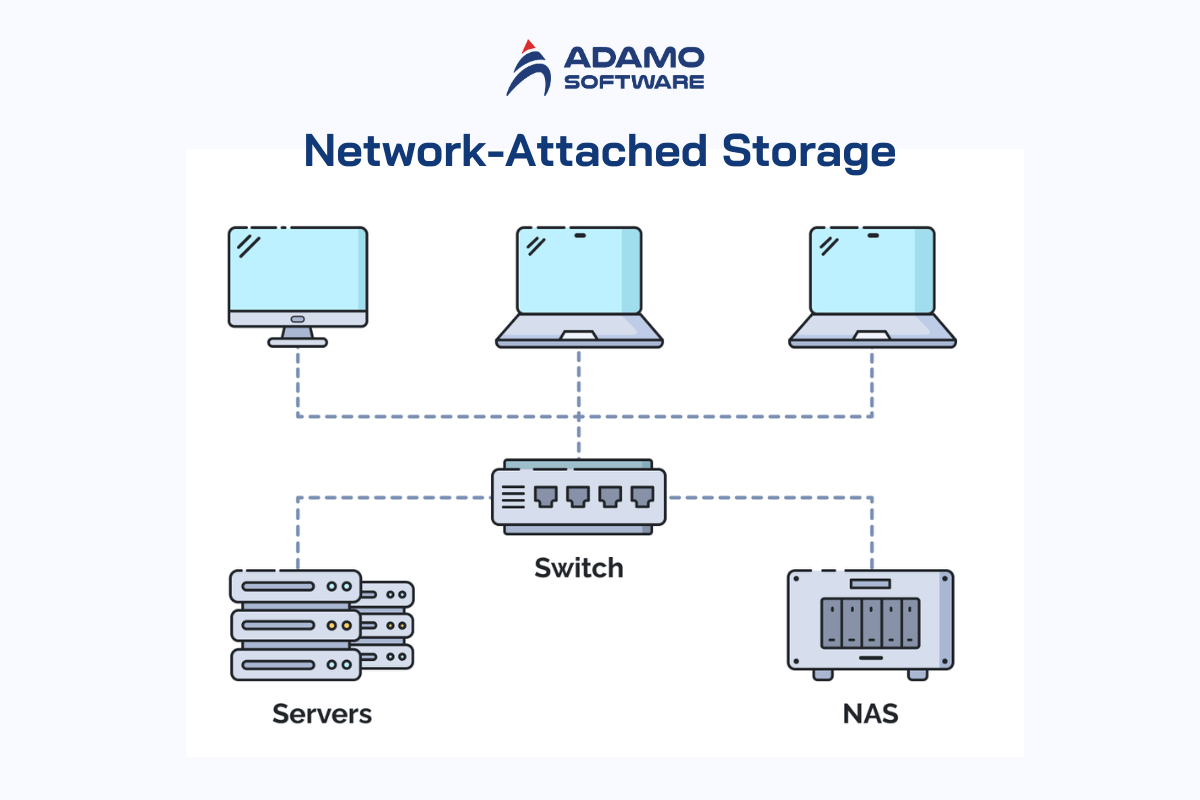
2. Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS is a single storage device that provides data access to all devices on a network. Hospitals connected to a local area network (LAN) can retrieve data from centralized disk capacity using an Ethernet connection.
_ Benefits of NAS for hospitals include:
_ High-performance data exchange
_ Strong access control and security
_ Data resiliency provided by RAID arrays
_ Easy setup and deployment
Hospitals with large volumes of data use NAS to support collaboration between departments.
3. Storage Area Network (SAN)
SAN data storage solution is a high-performance network of storage devices accessible by multiple servers or computers through dedicated fiber channel pipelines. SAN allows the transfer of medical images and data directly from storage to workstations without burdening existing hospital servers. This helps to:
_ Avoid latency issues
_ Ease bandwidth burden
_ Speed up data transmission
_ Improve workflows within hospital departments
SAN performs best with a separate, private Ethernet network between the server and clients, keeping file request traffic out of the fiber channel network and providing near real-time access to picture archiving and communication systems (PACS).
Public Data Storage
While storing your corporate data onsite may seem secure, on-premises storage can be quite costly. For SMEs, the expenses of private data storage often outweigh the benefits, prompting many organizations to seek more efficient, scalable solutions like cloud-based storage.
If you’ve ever accessed data “in the cloud,” you’ve used public data storage. Known as cloud storage, this method moves your data to a remote data center, making it accessible wherever you have an internet connection.
1. Cloud Storage (Public Version)
Hospitals migrate data to the cloud to reduce the costs of maintaining on-premises physical data centers. This flexibility in server space purchases has contributed to the healthcare cloud computing market’s expected growth to around $40 billion by 2026, with an annual growth rate of 14% from 2019 to 2026.
In addition to cost savings, moving to the cloud offers:
_ Faster, safer, and easier health information exchange (HIE)
_ Compliance with government regulations and enhanced data safety
_ Quicker backup and recovery processes
_ Automated back-end operations
_ Easy expansion options
But migrating healthcare data to the cloud isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The rapid data growth pushes healthcare companies to reevaluate their infrastructures and storage options, leading to new challenges.
2. Colocation Services
Data colocation, or “colo,” involves storing your data hardware in a shared, secure space known as a colocation data center or third-party data center. Like renting a storage unit, a business rents space in the colocation facility for their equipment, while the company manages necessary maintenance such as temperature control, physical security, and bandwidth needs.
Colocation data storage solution offers higher, more reliable uptime, often based on service tiers, allowing businesses to scale their data storage needs as they grow without dedicating additional staff and resources. Colocation also provides greater security than standard on-premises methods, with measures like 24/7 camera surveillance and biometric access controls.
But if your colocation facility is not carrier-neutral, your connectivity options may be limited. When considering colocation services, ensure the provider offers all the services your business might need as it expands.
Hybrid Data Storage
As the name implies, hybrid data storage combines private and public data storage methods to highlight the benefits of both options. Often managed by your IT department or a managed IT services provider, hybrid storage enables you to protect your data from unauthorized access while minimizing the maintenance required.
1. Cloud Storage (Hybrid Version)
Hybrid data storage solution combines the best features of on-premises and cloud storage. In hybrid storage environments, health data maintains flexibility, scalability, performance, and control at a low cost. A healthcare organization uses both on-premises and cloud storage to maximize the benefits of each. Sensitive data can be stored on-premises for maximum control, while less sensitive data is housed in the cloud. This approach allows healthcare IT leaders to prioritize, monitor, and protect sensitive assets more efficiently without exhausting resources on less sensitive data that can be managed in the cloud.
2. Nimble Storage
Nimble storage is a modern data storage method that uses flash storage and predictive analytics to future-proof your business in the evolving digital landscape. Unlike the flash storage common in smartphones, laptops, and services, nimble storage is designed to provide flexible and reliable enterprise storage, ideal for SMBs with changing IT needs.
Nimble storage’s predictive analytics compares your IT issues with previous cases to resolve problems with proven solutions, streamlining your overall IT infrastructure and reducing downtime. Additionally, nimble storage offers six nines (99.9999%) availability, ensuring that your team can access data whenever they need it.
III. How to Choose the Best Data Storage Solution for Your Healthcare Organization
Choosing the right data storage solution becomes increasingly essential as healthcare organizations generate more data. Here are some key considerations when selecting data storage solutions for your hospital:
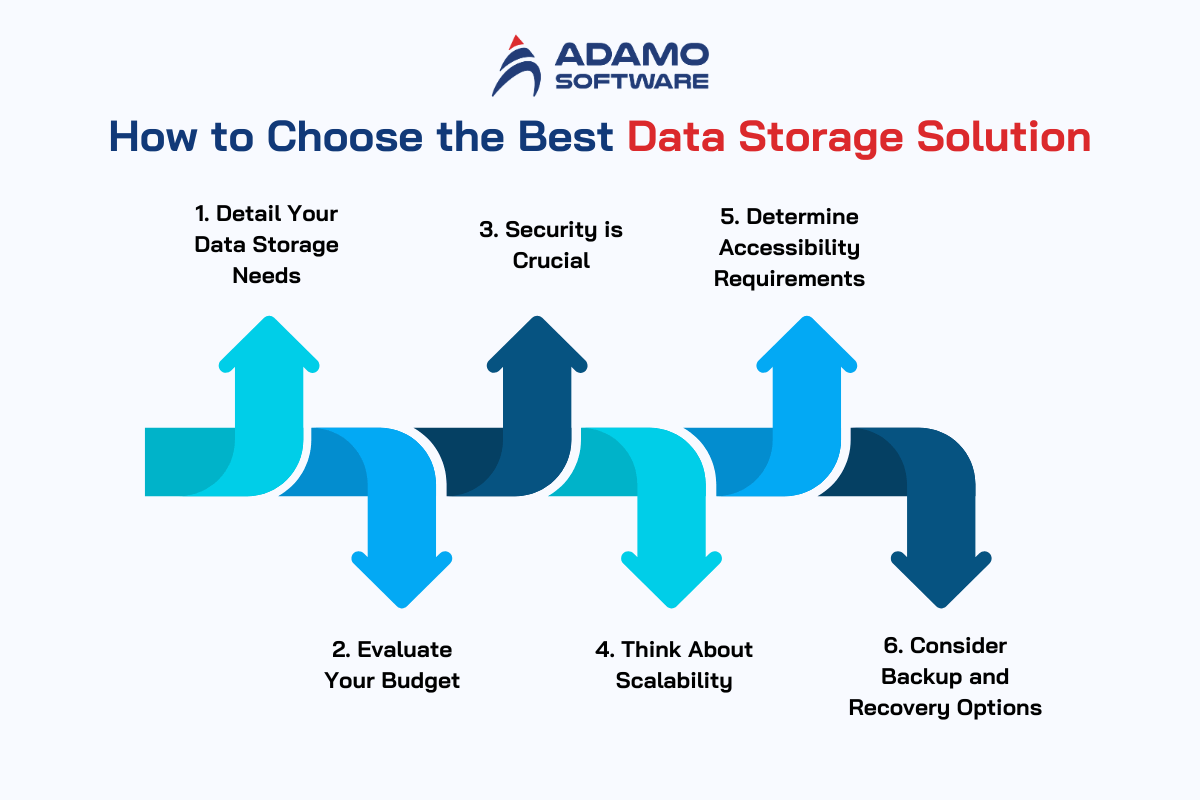
1. Detail Your Data Storage Needs
Start by assessing your storage needs based on the size of your healthcare organization, the amount of data you generate, and the type of data you need to store. For instance, a small clinic generating a few hundred megabytes of data annually might suffice with an external hard drive. In contrast, a large hospital with terabytes of data may require a more sophisticated storage system.
2. Evaluate Your Budget – How Much Can You Spend
Budget is a critical factor in selecting a data storage solution. Storage options vary widely in price, so determine your spending limit before deciding. Keep in mind that while some solutions may have higher upfront costs, they might be more cost-effective in the long run due to their durability, scalability, or other benefits.
3. Security is Crucial
Data security is paramount in healthcare. Choose storage solutions with strong encryption, firewalls, and other security features to protect your data from unauthorized access. Ensuring data security is essential for maintaining patient confidentiality and compliance with regulations.
4. Think About Scalability
As your healthcare organization grows, your data storage needs will likely increase. Opt for scalable storage solutions that can expand with your business. Cloud storage, for example, is highly scalable and can easily adapt to changes in storage requirements over time.
5. Determine Accessibility Requirements
Consider how your team will access the stored data. Will access be required from multiple locations or just a single site? Is remote access necessary? Ensure that the storage solution you choose meets your accessibility needs and supports your workflow.
6. Consider Backup and Recovery Options
Backup and recovery capabilities are crucial for safeguarding data. Choose storage solutions that offer regular backups, data redundancy, and other features to protect your data in case of hardware failure or other issues. Robust backup and recovery options ensure continuity and data integrity.
Also read: What is Health Data Management? Benefits, Challenges and HDM Software
IV. Current Trends in Data Storage in Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry isn’t the only sector experiencing a major transformation in data storage and the need for secure, strategic data management systems. The trends covered in this section are shaping the future of data storage across all industries, changing how organizations collect, manage, store, and share their data.
1. Cloud Migration
The shift toward cloud-based data storage solution in healthcare has been substantial over the past several years. Cloud storage offers remarkable flexibility, enabling healthcare providers to scale their storage resources as needed. It also provides centralized storage and remote access capabilities.
Amish Patel, CTO of Fortune 20 healthcare company Elevance Health, recently highlighted the transformative impact of storing and operating data on the cloud in an interview with McKinsey. “By leveraging cloud-native approaches,” he shared, “we have achieved agility, scalability, and resiliency in our member-facing applications.
This ‘single-pane-of-glass’ approach to standardization has significantly enhanced member experiences and streamlined processes, giving us a competitive advantage.” This competitive edge will be increasingly crucial as patients behave more like consumers and seek personalized, high-touch experiences from their providers.
2. Big Data and Analytics
Big data analytics plays a crucial role in healthcare data storage by enabling valuable insights from vast datasets. With the increasing availability of electronic health records (EHRs) and third-party data, big data analytics can identify patterns and trends that inform smarter clinical decision-making.
Analytical approaches help healthcare organizations minimize risk, predict patient outcomes, improve diagnostics, and enhance population health management. Leveraging big data allows healthcare providers to better understand patient needs, leading to more personalized and effective care at scale.
To achieve these capabilities, organizations need unified storage solutions that provide central access to their datasets for performing analyses and making decisions.
3. AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are increasingly integrated into healthcare data storage solution systems, fundamentally changing the level of care provided. AI-powered predictive analytics can anticipate disease occurrence before symptoms advance, detect patterns that humans alone can’t discern, quickly summarize large datasets, and mine vast amounts of data to identify population-level trends. From a data storage perspective, AI enhances the value of having data centralized in a single repository where AI technologies can access and analyze it.
These trends are not only shaping the future of data storage in healthcare but also setting a precedent for other industries. Healthcare organizations must adopt these advanced data storage solutions and approaches to stay competitive and meet the evolving demands of their customers and patients.
V. Final Thoughts
Data storage and management are foundational elements in the healthcare industry. Adhering to best practices in these areas is crucial, as they underpin every aspect of healthcare, from patient care to clinical decision-making. A robust data storage solution, combined with effective backup and disaster recovery plans, offers critical protection against unforeseen events like cyberattacks.

Comprehensive data protection involves a holistic approach, including governance, technologies, strategies, and regulatory frameworks. Seamless integration and interoperability further enhance coordination and operations throughout patient care. Ultimately, the quality of care and the security of patient information are deeply connected to the efficiency of data storage and management practices.
With over six years of experience building complex healthcare software development solutions, Adamo Software is well-equipped to help your organization optimize data management and harness the power of the cloud. Contact us today to make your data work for you.
FAQs
1. What are the best storage platforms for the healthcare industry?
The top healthcare-ready storage platforms include AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Box for Healthcare, FileCloud, Sync.com, and Wasabi. These platforms offer secure, scalable storage with encryption, HIPAA/GDPR compliance, audit controls, and support for medical data formats—making them suitable for clinics, hospitals, and growing health networks.
2. What are some user-friendly medical records storage tools for people with limited tech skills?
Easy-to-use options include OneRecord, MyDigiRecords, Capzule PHR, MyMed, and KeepTrackMed. These apps offer simple interfaces, mobile access, and secure storage, making it easy for non-tech users to save, view, and share their medical records. Cloud tools like Sync.com are also helpful for storing basic PDFs and images securely.





