What is data tokenization technology? How to strengthen payment processing security

Tokenization technology protects sensitive data such as credit card numbers and bank account numbers during the transaction process.
In a business environment characterized by rapid change, numerous innovations emerge, some of which are immediately useful while others quickly disappear. As for tokenization technology, it is no longer a buzzword but rather a phenomenon that requires further explanation.
Tokenization technology not only increases the security of sensitive data, but it also reduces the scope and associated costs of compliance. The adaptability of tokenization technology enables businesses to develop custom solutions that help them balance their data utility and security demands.
I. What is data tokenization?
Data tokenization is the process of transforming sensitive data into a token or unique identifier while maintaining its value and connection to the original data. This token represents the actual data and facilitates its use across multiple systems and procedures without disclosing the sensitive data.
Since sensitive data remains secure even if the token is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties, tokenization is frequently used as a data privacy-protecting security mechanism. The original sensitive data is protected, while the token may be used for authorized purposes, such as data analysis, storage, or sharing.
In a secure context, a token can be momentarily connected to the original data when it is used in a transaction or activity. This prevents the exposure of sensitive information while allowing authorized systems or applications to validate and process tokenized data.
II. How does tokenization work?
Tokenization technology replaces sensitive data with equivalents that are not sensitive. A token refers to the replacement information. This may employ any of the following procedures:
_ With a key, a theoretically reversible cryptographic function.
_ A function that cannot be inverted, similar to a hash function.
_ An index function or a randomly generated number.
Therefore, the token will become the exposed information, while the sensitive data that it represents is securely stored on a centralized server known as the token vault. Only within the token vault is it possible to trace the original information back to its corresponding token.
Tokenization technology in payment processing involves substituting a credit or debit card or account information with a token. Tokens have no intrinsic value and are not associated with any account or person.
The 16-digit primary account number (PAN) of the customer is substituted with a randomly-generated, unique alphanumeric ID. This eliminates any link between the transaction and the material, thereby reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and making it ideal for credit card transactions. Tokenization technology of data stores credit card and bank account information in a virtualized compartment, enabling businesses to transmit data over computer networks in a secure manner.
As previously remarked, some tokenization is faultless. Instead of storing sensitive information in a secure vault, vaultless tokens utilize an algorithm to retain the data. If a token is modifiable or reversible, the original sensitive data is typically not stored in a vault. Due to its inferior security, this technique is rarely employed.
III. Benefits of tokenization to explain why tokenization is important
Tokenization technology can provide several significant advantages for protecting sensitive consumer data.
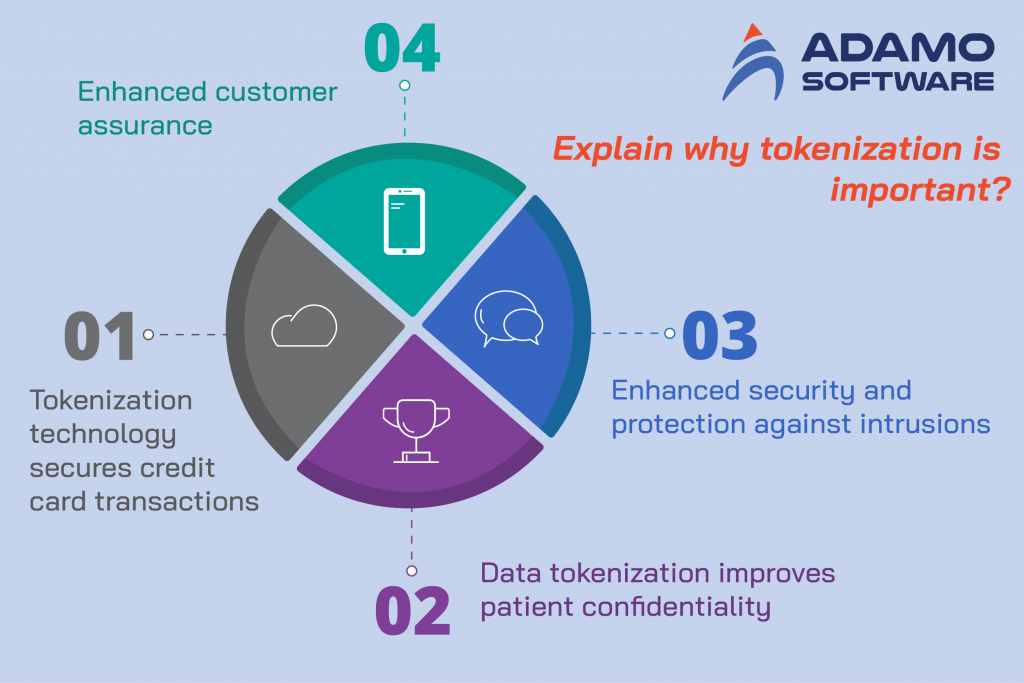
1. Enhanced customer assurance
Tokenization technology adds an extra layer of security to eCommerce websites, boosting consumer confidence.
2. Enhanced security and protection against intrusions
By using tokenization technology, businesses are no longer required to record sensitive data in their input terminals, store it in internal databases, or transmit it through their information systems. This protects businesses against security breaches.
3. Data tokenization improves patient confidentiality
Organizations can use tokenization technology for HIPAA-compliant scenarios (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). By substituting tokenized values for electronically protected health information (ePHI) and nonpublic personal information (NPPI), healthcare organizations can better adhere to HIPAA regulations.
4. Tokenization technology secures credit card transactions
The payment card industry must conform with stringent regulations and standards. Tokenization technology solutions protect cardholder information, including magnetic swipe data, primary account number, and cardholder information. Companies can more easily comply with industry standards and protect client information.
IV. Data & Tokenization example explained
When a merchant processes a customer’s bank account information, the PAN (Primary Account Number) is replaced with a token. Replace 1234-4321-5678-8765 with, for example, 67h%$877F49hUa.
The merchant can use the token ID to maintain customer records, for example, 67h%$877F49hUa is associated with Kevin Smith. The token is then sent to the payment processor, which de-tokenizes the ID and verifies the payment. The number 67h%$877F49hUa is now 1234-4321-5678-8765.
The token is only readable by the payment processor; it has no value to anyone else. Moreover, the token is only valid for use with the given merchant.
V. Tokenization transaction with debit cards and credit cards
Card information is stored in eCommerce sites or purchasing apps on mobile devices and tablets during online shopping. This is because when consumers pay with credit cards, the merchant stores their information. In contrast, tokenization technology replaces the credit and debit card information with an alternative identifier known as a “token.”
When a cardholder initiates a payment request, the data is sent to a bank registered in the token system. The token requestor then transmits the token for the authorization to the card network. After authorization, the data are stored in the bank’s secure archives, and the token is compared to the user’s PAN. The bank verifies the information and determines whether or not to accept the tokenization technology.
After successful authentication, the token is returned to the merchant for future transactions. As soon as the tokenization technology procedure is complete, however, customers’ personal information is protected from cybercriminals.
Also read: PaaS: A Boom of Payment as a Service in Outsourcing Payment Market
VI. Differences tokenization vs. encryption
While both are excellent instruments for preventing credit card fraud, tokenization and encryption are frequently confused. Consequently, what is the distinction between tokenization and encryption?
Encryption is a type of cryptography that safeguards sensitive information by transforming it into unreadable code. A system employing a sophisticated encryption algorithm replaces each number, letter, and blank space on a card with a different one.
This encoded data should be decrypted using the key or password provided at the conclusion.
The biggest difference between tokenization and encryption is that encryption is reversible. If you know the algorithm behind the encryption, it is always possible to encrypt information.
Since encrypted data is “breakable,” the PCI Council still considers it to be sensitive. Thus, meeting compliance requirements with encryption is considerably more expensive than with tokenization.
Encryption is one of the most secure methods for safeguarding card data during transactions where the card is tangibly present. Nevertheless, tokenization technology provides significantly greater security for payments made with expired cards.
Specialists recommend combining encryption and tokenization to better protect sensitive data in transit and comply with PCI DSS requirements.
VIII. Tokenization technology: potential to apply in various fields
Tokenization technology has vast application potential and can be utilized in various fields.
1. Real estate
Real estate is a vast and expensive market, making it difficult for inexperienced investors to participate in significant projects. With tokenization technology, multiple investors can own a part of a property, making real estate contributions more accessible to a wider audience. Moreover, tokenization technology streamlines the automatic distribution of income between stakeholders, addresses property-related rights such as inheritance, and facilitates liquidity for real estate transactions.
2. Asset management
When assets are tokenized, they can be subdivided, allowing potential investors to acquire even a fraction of a single share. By dividing securities, commodities, and other financial assets into smaller units, investors’ portfolios can be managed more but with greater flexibility.
3. Contracts
Tokenization technology allows for more efficient contract and agreement management. In such a system, digital tokens represent contractual obligations or terms, enabling more efficient agreement management through the automation of contract execution, verification of real-time obligations, and extension of existing agreements.
VII. Adamo Software Helps You Secure Your Payment Processes
The most effective method for mitigating the risk of a data intrusion is one that actively employs all of the best measures that have been demonstrated to provide superior protection, such as Adamo Software’s. Our resources are designed to facilitate the PCI DSS compliance process so that ISVs and merchants can easily determine the appropriate steps.
Contact Adamo Software for more information on what we can do for you right now. With the premier software development company in Vietnam, you can learn more about the options available to you.