What is EMR in Healthcare: Types, Features, Cost
Today, healthcare is rapidly becoming digital. Electronic medical records (EMR) have become standard in healthcare environments. Has it been a while since you last saw your doctor write something down on your physical chart? Many healthcare providers and facilities now rely on EMR to store crucial information about your health and well-being. EMR is a fundamental component of digital healthcare.
This guide will dive into a comprehensive analysis of what is EMR in healthcare, including common examples, key features, and costs.
I. What is EMR in Healthcare
Healthcare data is divided into three parts that can be used interchangeably. These are the Electronic Medical Record (EMR), the Electronic Health Record (EHR), and the Personal Health Record (PHR).
So, what is an EMR in Healthcare? In short, an EMR is a healthcare information technology solution such as software or a platform healthcare providers use to record all of a patient’s diagnoses and treatments.
An EMR contains demographic information, medications, allergies, vaccinations, test results, radiology reports, and visits. An EMR may also include billing information and insurance information. Essentially, an EMR is like a digital version of a patient’s medical history, containing all records of a patient’s past medical care.
II. EHR Vs. EMR: What is the difference?
The healthcare industry uses many acronyms, such as EHR and EMR, which are often used interchangeably. Though they’re similar, they have different meanings. EHR refers to electronic health records, while EMR means electronic medical records. EHRs cover a wider and more comprehensive range of information compared to EMRs.
In this guide, we’ll discuss the similarities and differences of EHR vs. EMR as well as the role each has in healthcare record keeping.
1. Electronic medical records (EMR)
EMR is the digital version of a clinician’s paper chart used in a healthcare provider’s office. They store comprehensive medical and treatment histories for patients within a single practice. Compared to paper records, EMRs offer significant benefits. For instance, they allow healthcare providers to:
- Track patient data over time
- Quickly identify patients needing preventive care or routine checkups
- Monitor specific health metrics like blood pressure or vaccination status
- Enhance the quality of care within the practice
However, EMR has limitations in sharing information outside the practice. Often, patient records must be printed and physically sent to specialists or other healthcare team members, making them somewhat analogous to paper records in terms of data sharing.
In contrast, EHR healthcare is built for interoperability, allowing various systems to exchange and use data. This capability is essential as it grants providers access to a patient’s complete medical history, even when multiple providers are involved.
2. Electronic health records (EHRs)
EHRs offer a comprehensive view of a patient’s health, going beyond the typical clinical data collected at a healthcare provider’s facility. They are designed to extend beyond the organization, gathering and integrating information from various sources.
EHRs facilitate information sharing with different healthcare providers, such as laboratories and multispecialty clinics, enabling them to store and access data from all physicians involved in patient care.
According to the National Health Information Technology Alliance, EHR data “can be created, managed, and accessed by clinicians and authorized staff across many healthcare organizations.” This system allows patient information to follow the patient to specialists, hospitals, nursing homes, and even across the country. HIMSS Analytics highlights that EHRs enable convenient sharing of medical information among stakeholders, allowing patient information to accompany them through various stages of care.
EHRs are designed to be accessible to everyone involved in a patient’s care, including the patients themselves, as emphasized in the Phase 1 definition of “meaningful use” of EHRs. This accessibility makes EHRs unique because secure information sharing enhances trust. Healthcare is a collaborative effort, and shared information is essential to that collaboration. The value of the healthcare delivery system largely depends on the effective communication of information among all parties, facilitating a collaborative information exchange.
Here are some of the main differences between electronic health records and electronic medical records:
| EMR | EHR |
| A digital version of a patient’s medical chart.
| A digital record encompassing a patient’s overall health.
|
| Not designed for sharing outside a single practice. | Can be shared with multiple healthcare organizations.
|
| Patients cannot take their EMRs to other practices.
| Patients can carry their EHRs to share with other specialists.
|
| Focuses primarily on diagnosis and treatment by one provider.
| Accessible by various specialists beyond a single provider, ensuring comprehensive care and treatment.
|
III. Common Types of Electronic Medical Record
There are different types of healthcare EMR software available in the market. You can choose the type of EMR based on your needs. There are some EMR that cater to the specific needs of hospitals, while there are many that cater to healthcare providers.
Here is a list of the top common types of electronic medical records:
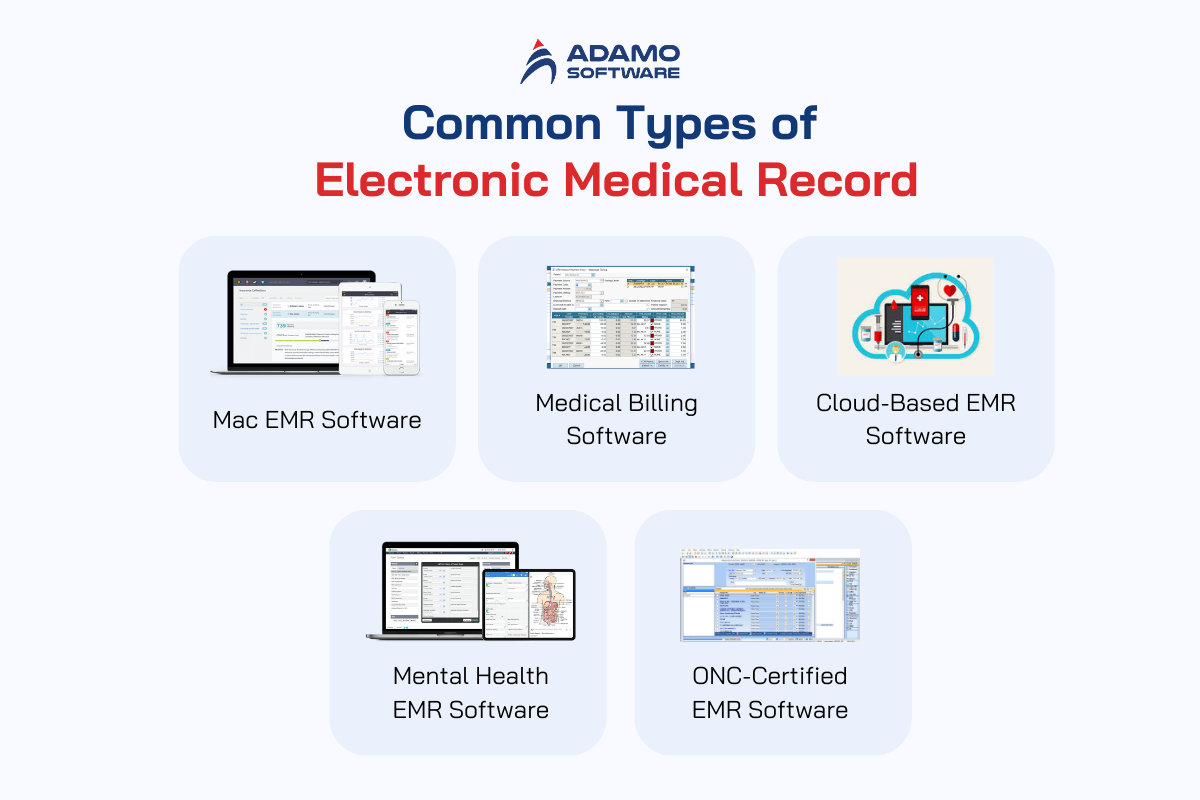
1. Mac EMR Software
As the name suggests, this is an EMR software specifically designed for Mac Operating System (MacOS) or Macintosh Computer users. This software offers unique Mac features, allowing users to easily access their medical data on any Apple device with an Internet connection.
2. Medical Billing Software
EMR records the entire patient treatment cycle in a hospital. This software easily integrates with the medical billing system for better management. It includes various billing functions such as claim validation, billing, insurance, and payment. It also supports other financial transactions without having to deal with paper systems. This reduces the administrative burden on clinics by processing payments through an automated system.
3. Cloud-Based EMR Software
Cloud-based EMR software is a widely used type of EMR that provides online data accessibility, enabling remote use. Most of the cloud storage technology supports good SaaS EMRs. Cloud technology enhances data storage and security by storing all information on remote servers, providing stronger protection and reliability. Moreover, this cloud storage technology gives EMR systems more special capabilities. The cloud offers advantages such as greater scalability, ease of use, cost efficiency, and secure data-sharing capabilities.
4. Mental Health EMR Software
These EMR solutions offer workflows for mental and behavioral health providers and counselors to manage patients. This EMR software is tailored to mental health clinics, therapists, and related teams’ needs. Additionally, the note management feature of this EMR makes it easier for therapists or doctors to access their notes.
5. ONC-Certified EMR Software
These EMR software programs are certified by the US Government’s Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). This certification guarantees that the software meets the meaningful use standards for health information established by the ONC.
Also read: Top 15+ EMR Integration Solutions in 2024 for healthcare industry
IV. Key Features of EMR System
Electronic medical records are increasingly popular and becoming important for effectively managing patient medical records and providing better healthcare services. With powerful technologies, including Big Data and predictive analytics, modern healthcare organizations have many options for EMR software development.
Let’s analyze the main features of EMR and their impact on the workflow of medical facilities.
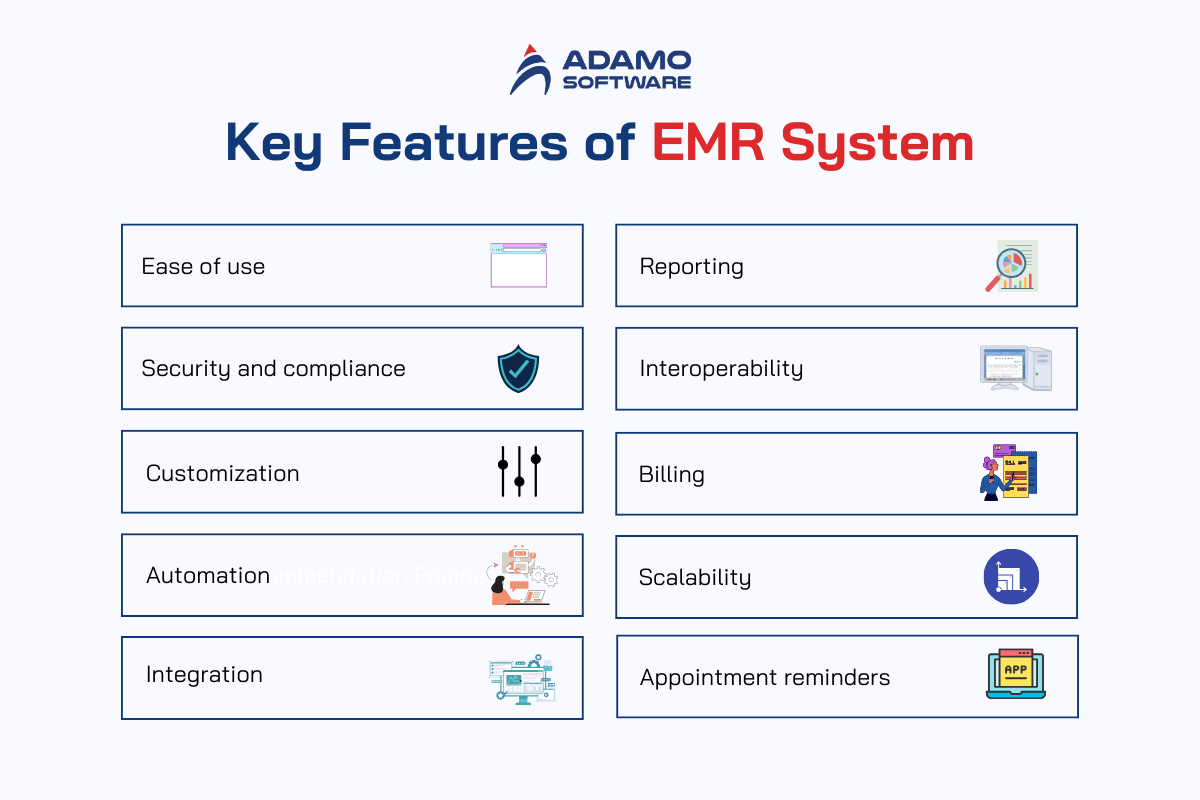
Feature 1: Ease of Use
Your EMR software should be easy to understand, easy to use, easy to navigate, and take little time to get to grips with. In addition to being intuitive, the tool must have a user-friendly interface. That’s because users want to access their medical records quickly and easily, enter the necessary data, and review them without much effort.
Feature 2: Security and Compliance
EMR tools must provide a robust environment for storing and accessing information, primarily when using the cloud in patient record data management. The key patient data security requirements in such a scenario are data encryption, provision of access control, authentication, and auditing. You should ensure HIPAA compliance to keep your data safe.
Feature 3: Customization
With the right EMR system, you can customize the user interface, add and remove desired features, and provide custom security protocols. At the same time, customization includes the ability to change user roles and access levels as well as the opportunity to configure the EMR software to fit the organization’s workflow.
Feature 4: Automation
Automating as many tasks as possible, like patient requests, appointment scheduling, and data entry, is essential. So, by leveraging the potential of automation based on AI and Machine Learning, you can reduce the time and effort required to manage patient data and allocate them to more urgent tasks.
Feature 5: Integration
You will be able to integrate your EMR tool with other clinical systems and technologies such as clinic software, laboratory software, payment gateways, and healthcare information systems. That allows for simplified departmental coordination, minimizing human errors and miscommunication.
Feature 6: Reporting
Statistical reporting is a very important feature to improve the quality of information collected and processed by EMR software. It automatically compiles reports on medical data, demographics, treatment plans, diagnoses, and more. Healthcare facilities can seamlessly track patient progress and make informed decisions with excellent reporting options.
Feature 7: Interoperability
Interoperability is the feature of an EMR tool interacting with other systems and exchanging valuable data, including integrating third-party applications, connecting to medical devices, and more. Helps share patient data within and across healthcare organizations with maximum effort.
Feature 8: Billing
Billing software helps healthcare providers accurately track and bill patients online for services provided. Additionally, the billing feature helps manage patient accounts, allowing them to be updated and bills completed on time. That prevents costly medical payment delays associated with denied claims and increased administrative costs.
Feature 9: Scalability
Your healthcare facility may handle more patients and operate more staff in the future, so your EMR software must be scalable as your organization grows. Additionally, the tool may need to adapt and comply with changing regulatory requirements.
Feature 10: Appointment Reminders
With electronic medical record EMR software connected via email across mobile devices, tablets, and laptops, the ability to stay in touch with your patients is at all times. Appointment reminders allow you to take advantage of this level of connection by sending automatic reminders to patients.
Patients will receive initial notification of an upcoming appointment, a reminder seven days in advance, and again 24 hours before the scheduled appointment. Automating this task saves significant time for practice management clinics and reduces missed appointments.
Also read: Impact of Electronic Medical Records in Healthcare – 9 Advantages
V. How Much Does It Cost of EMR System
When it comes to answering the question, “How much does EMR system cost?” there is no simple answer because it depends on many factors.
Several factors must be considered before choosing an EMR system. The development cost for a health app or medical software is often very high. As a result, many software companies do not disclose the cost of their EMR systems upfront. Instead, they encourage potential customers to contact their sales teams for pricing information.
So, be sure to conduct thorough research before choosing a vendor for your EMR system. There are two main types of EMR cost structures based on their availability:
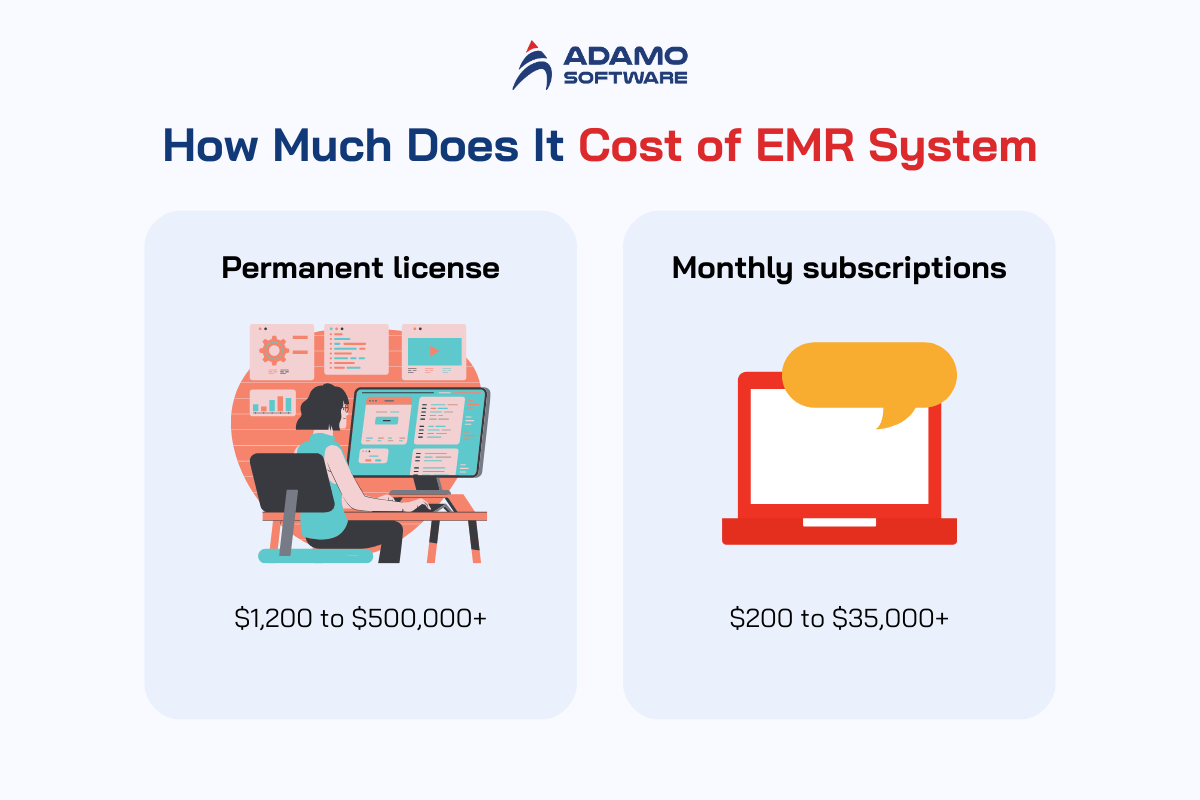
– Permanent license
As the name suggests, this pricing model gives you lifetime ownership of the EMR software once you’ve made the full payment. This approach is typically used for on-site implementations, where the software is operated and maintained on your practice’s servers.
The upfront cost for owning the license can range from $1,200 to over $500,000. Besides the initial payment, there are ongoing monthly maintenance fees, along with potential hidden costs for integration and customization.
You might also need to hire IT staff to effectively manage and maintain the software on-site.
– Monthly subscriptions
This payment model allows you to pay a monthly fee to use the EMR system for a set period. It does not grant you ownership of the software. Typically, this approach uses a cloud-based EMR system, which is ideal for remote practices as it allows easy online access to data.
In addition to an initial installation fee, monthly subscription costs range from $200 to over $35,000, depending on the system and features selected.
There could also be extra hidden costs for customization, integration, and additional storage space.
VI. Adamo – A Trusted Partner for EMR in Healthcare Development
In summary, EMR and EHR systems are now essential to modern healthcare. They enable doctors to oversee patients remotely, either through a physician dashboard or through technologies like remote therapeutic monitoring.
At Adamo, we excel in developing innovative EMR solutions for the healthcare industry. We are offering game-changing EMR in healthcare software development services with our experts to enable optimum medical care and clinical outcomes. Our focus on quality and innovation ensures we are a dependable partner for healthcare providers improving their digital infrastructure.
Our EMR solutions are designed to streamline healthcare workflows, improve data accuracy, and ensure compliance with industry standards. We focus on providing a seamless experience for healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver better patient care. We ensure our software solutions are reliable and effective by incorporating advanced features and maintaining top security and usability standards.
VII. FAQs about Electronic Medical Record
What does EHR stand for in healthcare?
In healthcare, EHR stands for Electronic Health Record. It is an electronic record of a patient’s medical history. EHRs include information like diagnoses, medications, and test results. They help doctors and nurses access and share patient data easily.
What does EMR stand for in healthcare?
In healthcare, EMR stands for Electronic Medical Record. It is a digital version of a patient’s medical chart. EMR contain details like medical history, diagnoses, and treatment plans. They are used by doctors to track patient care.
What is EMR experience in healthcare?
EMR experience in healthcare means familiarity with using electronic medical record systems. It involves managing patient data digitally. This experience includes tasks like recording medical histories and updating treatment information. It helps improve patient care and data accuracy.
What are the benefits of using an EMR?
Using an EMR system offers numerous benefits, including improved accuracy and accessibility of patient information. It enhances communication and coordination among healthcare providers, leading to better patient care. EMR also streamlines administrative processes, reduces paperwork, and ensures data security, protecting patient information from unauthorized access. Overall, EMR contributes to a more efficient and effective healthcare system.
Is patient information secure in an EMR?
Patient information in an EMR is generally secure. EMR systems use encryption, access controls, and other security measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access and ensure privacy. However, healthcare providers need to follow best practices and regulatory standards to maintain the highest level of security.
Clinical Cost of a New EMR System
The cost of implementing a new EMR system can vary widely due to multiple factors. However, studies suggest that a physician might need to invest around $163,765 for the setup.
Components and Benefits of Typical EMR Systems
Typical EMR systems in healthcare encompass all essential databases needed for physicians to collect information. These systems save time and money by centralizing data, making it easily accessible for both doctors and patients.