Impact of Electronic Medical Records in Healthcare – 9 Advantages
The adoption of Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) has transformed the healthcare industry, offering numerous benefits and efficiencies. As digital versions of paper records, EMRs streamline the management and sharing of patient information, improving the quality of care and enhancing collaboration among healthcare providers.
By centralizing patient data, EMRs reduce errors, speed up treatment decisions, and support better health outcomes. So, the growing impact of electronic medical records in healthcare makes them a valuable tool. However, alongside the positive effects, they also pose challenges that must be addressed quickly. In particular, there are concerns about data security and the need for proper integration across different healthcare systems.
In this article, we will explore the impact of electronic records in healthcare on the quality of care and any supporting evidence. Highlight nine advantages and related FAQs about the impact of electronic medical records on healthcare.
I. Understanding the Basics of EMR
To understand exactly what the benefits and impact of electronic medical records in healthcare are, you first need to understand what they are.
1. Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
An EMR system is a platform designed to manage operations and store electronic medical records. Among its advantages is improved information sharing, which enhances the quality and effectiveness of integrated healthcare, supports health policy development, and advances medical education and research. However, the system faces significant challenges, including vocabulary standardization, security, privacy, and data quality concerns.
One of the most pressing issues with current EMR systems is the rapid expansion of healthcare data. The uncontrolled and exponential growth of information systems in the healthcare industry, both in size and diversity, has led to a lack of standardized data, making linking, retrieval, and analysis difficult.
Additionally, many EMR systems lack the flexibility to meet the diverse information needs of researchers from various fields. Fortunately, data visualization or visual analytics offers promising solutions to the increasing issue of information overload.
2. Data Visualization and Linked Data
Data visualization, a science focused on analytic reasoning and the visual representation of data, has transformed data sciences by facilitating mapping and visualization, leading to better interpretations of complex information (Huang et al., 2015). Effective visualization provides an alternative method to illustrate potential data connections and relationships. Despite its application in various healthcare areas (Huang et al., 2015), data visualization has yet to be widely adopted in EMR data using the NoSQL graph model.
One key application of visualization models involves Linked Data, which employs uniform resource identifiers (URIs), hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP), and resource description framework (RDF/JSON) technologies. This approach is crucial for large-scale data integration on the web (Bizer et al., 2009). A prime example of a large Linked Dataset is DBPedia, which uses RDF-formatted content from Wikipedia to connect with other datasets on the web (W3C, 2015).
At present, the EMR systems in many hospitals store and distribute patient records across various databases, resulting in unwanted data redundancy and isolation. Linked Data systems, such as NoSQL databases, can provide a dynamic, graph-based model for recording and storing interchangeable data.
3. NoSQL (Not Only SQL) Databases
As data size and diversity in modern information systems increase exponentially, there is a growing need for more complex and extensive data structures than those managed by traditional relational databases. This necessity has driven the development of “NoSQL” databases. NoSQL architecture is designed to address the scalability, flexibility, performance, availability, and infrastructure cost limitations of relational databases (Stonebraker, 2009).
NoSQL systems rely on horizontal scalability, which enhances system performance by increasing the number of nodes, thus providing more computing capacity instead of boosting the power of individual nodes (Abramova and Bernardino, 2013).
Also read: What is EMR in Healthcare: Types, Features, Cost
II. Impact of Electronic Medical Records in Healthcare
EMRs are transforming the healthcare landscape by improving patient care, streamlining workflows, and improving data management.
In this section, we will explore the significant impact EMRs have had on healthcare. This includes benefits such as improved communication between providers, increased efficiency in administrative tasks, and improved patient outcomes. We will also address the challenges and considerations involved in effectively implementing EMR systems.
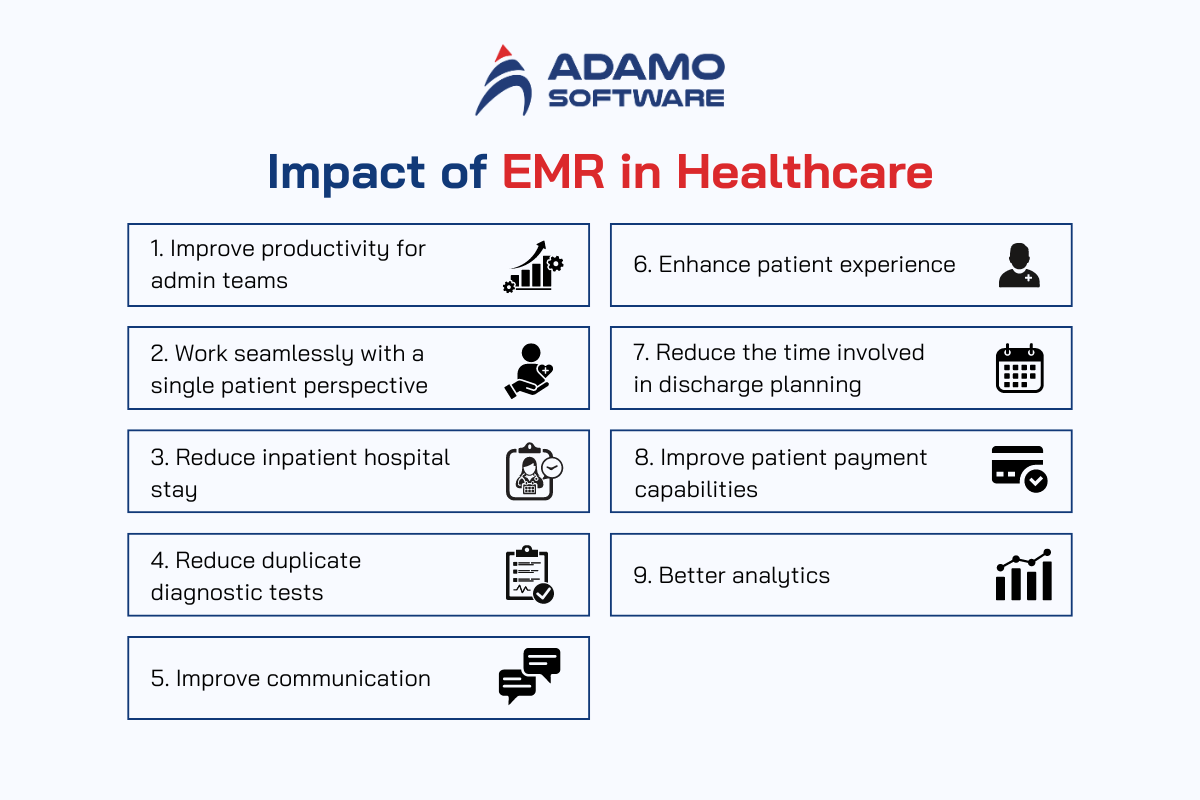
1. Improve productivity for admin teams
The impact of electronic medical records in healthcare is to improve productivity for admin teams. Medical, nursing, allied health and other medically affiliated staff no longer have to waste time sifting through reams of paperwork to get the information they need about patients. On the other hand, digitized records can be retrieved significantly more quickly and efficiently with just a few keystrokes. This function brings many benefits to both doctors and patients.
Today’s clinicians are also looking to use a single software application rather than open multiple systems to access the information they need to provide care.
Furthermore, because notes are no longer written on paper but are typed or selected from a menu of options in a predefined system, EMR software eliminates the problem of legibility.
Ultimately, time-saving strategies that reduce staff tasks and reduce operational costs while improving patient service can greatly benefit healthcare organizations.
2. Work seamlessly with a single patient perspective
One of the impacts of electronic medical records in healthcare is work seamlessly. Healthcare staff often work across multiple locations, receiving calls to advise patients on the ward or update prescriptions, which can now be done from anywhere. If they are located elsewhere, they can access patient records and complete prescriptions or review clinical notes to prioritize their work.
3. Reduce inpatient hospital stay
When utilized correctly, the impact of electronic medical records in healthcare reduces patient hospital stays. It allows patients to leave the hospital sooner, reducing exposure to germs and the possibility of having to return to the hospital. According to the results of one study, significant technology integration has the potential to free up clinicians and other important resources.
As more people seek medical services, this approach can invest more in infrastructure or hire more staff.
4. Reduce duplicate diagnostic tests
The impact of electronic medical records in healthcare includes reducing the frequency of duplicate diagnostic tests. Clinical information accessible in a single patient view means doctors can see what has been prescribed for the patient. This can reduce the ordering of duplicate diagnostic tests.
Electronic diagnostic systems can limit the types of tests required in a particular clinical setting, to ensure only subordinate staff request the most appropriate tests.
As a result, hospitals and healthcare organizations are increasingly implementing NUTS, or No Unnecessary Testing, especially pathology and imaging programs.
If the test is not clinically recommended, there is no evidence of benefit to the patient. It is better to move to another setting, such as an outpatient clinic.
Hospitals reduce inconvenience, discomfort, and potential harm to patients by ensuring patients receive evidence-based diagnostic tests that are valuable for clinical decision-making and are approved for the hospital environment.
5. Improve communication
Another significant impact of electronic medical records in healthcare is the improvement in communication. Engagement has not only improved, it has increased. The EPR/EHR system encourages communication and dialogue between healthcare professionals, departments, and the Trust. The speed of interaction with electronic messages is instantaneous, which is a huge improvement over paper communication through typed letters posted across a region or country.
There is also software that supports the communication element between software. Interoperability refers to the integration of healthcare solutions and the readiness of these computer programs to communicate information to other sources. In an ideal world, all solutions are integrated (via API) for complete transparency, the highest level of knowledge data about the patient and the EPR is trying to accomplish. show that.
6. Enhance patient experience
The impact of electronic medical records in healthcare extends to enhancing the patient’s experience. The patient portal not only provides patient notifications about scheduled appointments but is also a big plus because automated alerts minimize staff workload and phone calls.
Patients can interact with their medical providers, receive test results, and check their electronic medical records for accurate information or missing information through an active portal. moving continuously without stopping.
7. Reduce the time involved in discharge planning
The impact of electronic medical records in healthcare is evident in the reduction of time spent on discharge planning. A hospital’s responsibility to its patients does not end when the patient is discharged from the hospital. Hospitals must uphold and fulfill their responsibility to ensure that patients follow the treatment path that experts determine is appropriate for them to continue and complete. An effective EMR system can be instrumental in that.
Patients can be affected in many ways if the discharge process is incomplete, this is a critical time to transition to post-treatment care. However, with an EMR system, the discharge summary can begin as early as admission.
Ultimately, the discharge process is designed to provide patients with the knowledge and services they need to improve or maintain their health as they leave the hospital and avoid adverse outcomes and readmissions are not necessary.
8. Improve patient payment capabilities
The impact of electronic medical records in healthcare also includes improved patient payment capabilities. The health component of patient services is addressed with modern EMR software. The most suitable, web-based electronic health record solution, rather than a standalone platform, allows healthcare providers to complete billing and reporting requirements within the same system.
Ultimately, EMR customization is critical to developing a fully integrated system that helps you optimize revenue potential while reducing operating costs and improving private patient billing accuracy, so victims and patients are compensated.
9. Better analytics
Finally, the impact of electronic medical records in healthcare can be seen in the improvement of analytics. Analytics enable improved efficiency and coordination of care as well as reduce the administrative burden on your staff.
Data from various sources is combined into an integrated EMR data analytics interface, enabling efficient use of EMR data and ensuring smooth business operations through reports and dashboard numbers.
Ultimately, the right tools are essential for effective and consistent data analysis. The right technologies enable data and patient records to be analyzed and uncover additional insights that help deliver better care and optimize business processes.
III. How to Implement Electronic Medical Records
Begin by selecting an EMR system that matches the specific needs of your practice. Attending a demo and asking thorough questions will help you choose the best system for your requirements.

Once you’ve chosen your EMR system, create your login credentials and become acquainted with the interface and features. This will help you get comfortable with the system before full implementation. Proper training is essential for a smooth transition. Ensure that all staff members receive adequate training to use the EMR system effectively, which will help maximize its benefits.
Customize the EMR system by selecting templates and streamlining processes to capture all necessary information. This includes configuring options for recording patient histories, diagnoses, body charts, and practitioner notes.
Begin using the EMR system according to your plan. Monitor its performance and gather feedback from users to address any issues and make improvements as needed.
IV. Custom EMR Software from Adamo Software
With years of experience in premium healthcare software development outsourcing in Vietnam. We assist clients in developing cost-effective, enterprise-focused, and innovative mobile app solutions across various industries.
Adamo Software combines technical expertise with a deep understanding of the healthcare industry. Our dedicated team works closely with clients to create innovative, reliable, scalable EMR systems that integrate seamlessly with existing workflows. In addition, our software is designed to enhance patient care by streamlining data management, improving accuracy, and ensuring secure access to patient records.
V. Impact of Electronic Medical Records in Healthcare – FAQs
1. How does EMR improve patient care?
Electronic Medical Records significantly enhance patient care by providing healthcare providers access to comprehensive and accurate patient histories. This immediate access to a patient’s medical information is a key aspect of the impact of electronic medical records in healthcare. It helps reduce errors in treatment, such as incorrect medication prescriptions or misdiagnoses.
EMRs allow for real-time updates, ensuring that all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care have the most up-to-date information. This leads to more informed and timely decision-making, ultimately improving patient outcomes and the overall quality of care.
2. What are cost benefits of using EMR?
The use of EMRs can lead to substantial cost savings for healthcare organizations. By streamlining administrative processes, EMRs reduce the need for extensive paperwork, cutting down on clerical errors and the associated costs. Additionally, EMRs improve efficiency in billing and coding by automating many of these processes, which can lead to faster reimbursement from insurance companies.
Over time, the reduction in paper usage, storage costs, and the improved efficiency in managing patient information contribute to significant financial savings. This demonstrates the cost-effective impact of electronic medical records in healthcare.
3. How does EMR impact patient privacy and data security?
While they offer a positive impact of electronic medical records in healthcare, they also present challenges related to patient privacy and data security. The digitization of patient records makes them more accessible to authorized healthcare providers, which improves care coordination. However, this increased accessibility also raises concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential misuse of sensitive patient information.
To mitigate these risks, healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to protect patient data. Additionally, compliance with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is crucial to ensure that patient privacy is maintained.
4. Can EMR improve communication among healthcare providers?
Yes, EMRs greatly improve communication among healthcare providers by allowing seamless sharing of patient information. When different specialists, primary care physicians, and other healthcare professionals can access a patient’s EMR, they can coordinate care more effectively. This improved communication reduces the chances of duplicated tests, conflicting treatments, and other issues that can arise when providers are not fully informed.
As a result, patients receive more cohesive and well-coordinated care, leading to better health outcomes and a more streamlined healthcare experience.
5. What challenges do healthcare providers face when implementing EMR?
Implementing EMRs in healthcare can be challenging due to various factors, affecting the overall impact of electronic medical records. One of the primary challenges is the high cost associated with the initial setup, including the purchase of software, hardware, and the training of staff. The transition from paper records to EMRs can also be disruptive, as it requires significant changes in workflow and may temporarily affect the efficiency of the healthcare facility. Additionally, there can be resistance from staff who are accustomed to traditional methods and may be hesitant to adopt new technology.
Ongoing support and training are essential to ensure that staff are comfortable with the system and that the transition is as smooth as possible. Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of EMRs, such as improved patient care and operational efficiency, make the investment worthwhile.





