Ai in Manufacturing: Definition, Benefits, Use Cases, Challenges
To survive in the continuously and rapidly changing world market, manufacturers must embrace such technologies as AI. AI in manufacturing has been identified to encompass the areas of predictive maintenance, quality assurance, supply chain management, and manufacturing smart systems.
AI in manufacturing is the use of intricate formulas in solving problems, analyzing data, and arriving at decisions faster to automate various processes. This in turn enhances efficiency, and consequently, the quality of the products that are produced is better. Real-life applications show how AI is already making an impact in the manufacturing industry.
This article explores several key areas: It discusses what constitutes AI in manufacturing, how it is helpful, how it revolutionizes industries, some indications of where it is now, and the issues with it. We also define issues such as data quality, model accuracy, and workforce adaptation as issues and give ways to manage those issues.
I. What is AI in Manufacturing? Key AI Segments in Manufacturing
Integrated AI in manufacturing applies artificial intelligence to elevate the overall performance, productivity, and innovation in manufacturing firms. This refers to the use of artificial intelligence such as machine learning, computer vision, robotics, and other tools to automate actions and make decisions based on acquired knowledge. The use of AI in manufacturing is enhancing processes to be efficient and/or effective in their functioning.
Key AI segments in manufacturing include:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI helps in identifying patterns in sensor data, and reduces the chances of breakdowns, repair costs, and early retirements.
- Quality Control: It applies computer vision and deep learning to the face of a product to eliminate the chance of selling shoddy items to customers, thus improving the quality of the products sold, saving on costs, and hence customer satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI deals effectively with assets and schedules in making choices concerning inventory, patterns of demand, and logistics, hence an effective supply chain.
- Process Automation: Robotics and AI bring efficiency to work since they take over repetitive jobs, minimizing possible mistakes.
- Energy Management: AI thus works to ensure that the use of energy is done efficiently, hence cutting expenses while at the same time reducing the level of harm that is caused to the environment.
- Product Design and Development: AI mimics the real world, accelerating innovation and providing solutions for products much faster.
Applying AI in manufacturing makes it more accurate, dynamic, and competitive in a continuously changing environment. Applying artificial intelligence in the manufacturing industry causes changes in performing tasks, enabling operations to be efficient and imaginative.
II. Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
AI in manufacturing brings significant benefits, transforming traditional manufacturing paradigms and advancing the industry. By incorporating AI technologies, manufacturers achieve new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and creativity.
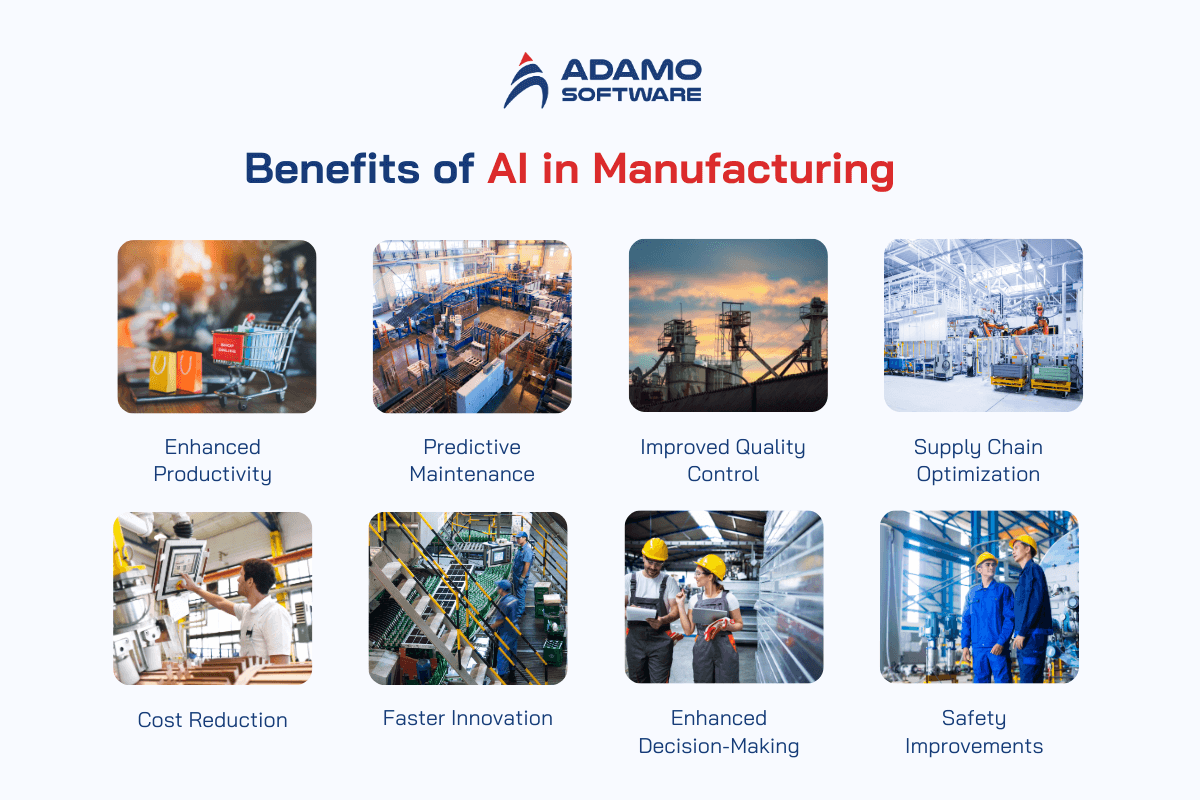
- Enhanced Productivity: AI-controlled automated systems operate on a gradual structure, and there is no pause in production. This fosters efficiency and effective utilization of resources, and hence the efficiency of the whole system is boosted.
- Predictive Maintenance: Mechanical failures are seen before they happen by AI systems within a car, through signal information. This eliminates production flare, wear and tear of equipment is slow, and hence it serves the company with a reduced average time to cover maintenance costs.
- Improved Quality Control: AI increases product quality by detecting defects or variations from standard patterns much better than human inspectors. This results in a lower number of substandard products, higher customer satisfaction, and less waste.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI enhances the capabilities of demand prediction, inventory management, and supply chain management by handling large amounts of data. It helps to keep replenishing the stock, which is required from time to time, while at the same time avoiding situations where lots of stockpiles are up and have to be disposed of by offering crazy discounts to get rid of it.
- Cost Reduction: Cost control is improved by AI, thus cutting operational costs through automation of processes, maintenance, and resources. Employment of this system also helps reduce energy costs since energy utilization is efficiently regulated.
- Faster Innovation: AI in manufacturing encourages shortening the time to produce a prototype of the product as well as test it. Techniques and frameworks utilizing machine learning help design numerous possibilities for a product to solve problems and decrease the pace of innovation.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI processes information in an exponential log and opens up results that humans cannot identify, thus improving decision-making at both corporate structures and functional unit levels.
- Safety Improvements: AI in manufacturing can improve workplace safety because they can do dangerous work and assess the security situation. Hazards to human employees are minimized since robots deal with potentially harmful substances.
III. The Ways AI is Transforming the Manufacturing Industry
Among the key areas impacted by artificial intelligence in manufacturing, one can identify such changes that the former brings to the latter as a strategic factor.
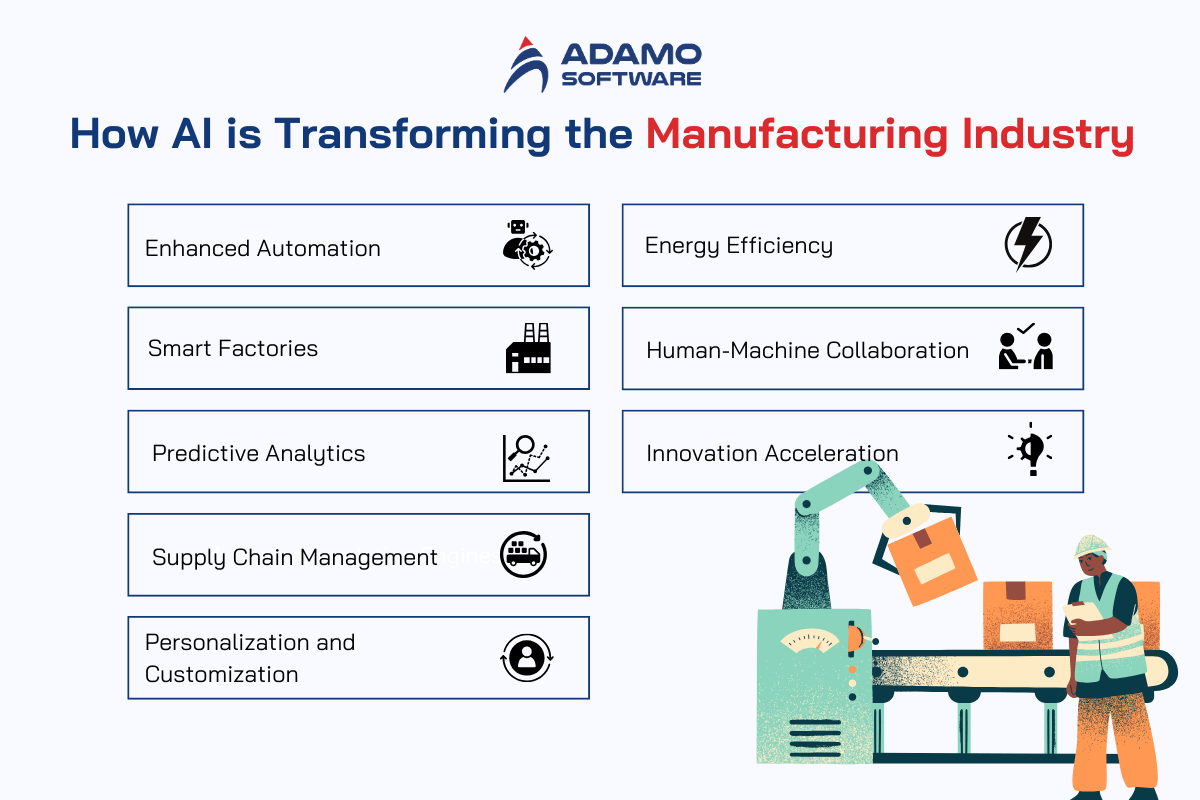
- Enhanced Automation: Technologies such as advanced robots and machine learning algorithms undertake various activities with better efficiency and proficiency than human beings and increase efficiency.
- Smart Factories: It introduces AI-powered systems in smart factories that collect and transmit information and are involved in the control of production processes at the same time. This makes the functioning effective and quickly identifies the problems that may arise.
- Predictive Analytics: It can be stated that AI defines predictive analysis regarding historical and real-time data sets. This enables one to predict trends, the likelihood of equipment failure, and when to undertake maintenance, thus decreasing operation costs and time spent on equipment.
- Supply Chain Management: The supply chain is enhanced through enhanced methods in demand planning, inventory management, and delivery. This eliminates several problems associated with stock and helps to design a more flexible supply chain.
- Personalization and Customization: AI in manufacturing gives special products to different consumers while being efficient, thus increasing their satisfaction levels and making them loyal.
- Energy Efficiency: In factories, AI measures and controls the conduct of power, lowering expenses and the sustainability of production.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: AI enhances workers’ efficiency by passing needed information at the right time and taking on routine work so the employees can perform more complex work.
- Innovation Acceleration: This is because, through AI, one can prototype and test out ideas and concepts without wasting time. Techniques like the above analyze designs and make recommendations on any weaknesses and possible enhancements to hasten product design and bring products to the marketing channel more quickly.
IV. AI in Manufacturing Examples and Use Cases
Based on different case studies, AI in manufacturing industry has exhibited its capacity to revolutionize the sector. These AI in manufacturing examples demonstrate how the various AI solutions are revolutionizing manufacturing practices and delivering added value. We will examine two significant real-life examples that demonstrate how AI is being applied to innovate in manufacturing.
Predictive Maintenance at Siemens
An industrial manufacturing giant, Siemens, has incorporated AI to transform its maintenance approaches. According to Siemens, through the use of predictive maintenance, they would like to minimize or, better yet, avoid equipment breakdowns.
Siemens uses AI in manufaturing to capture raw data from sensors placed on equipment for further analysis. These algorithms are used to make predictions on potential failures based on the patterns and outliers. Consequently, planned maintenance becomes possible instead of repair work, which reduces the amount of time when the equipment is not operational and also lowers maintenance costs. Consequently, this kind of application of AI makes sure that the machinery is effective and dependable, which in turn increases productivity.
The key learning from this case is how valuable data is to the organization in the instance of Siemens’ application of predictive maintenance. By analyzing the vast amount of data that accumulates during the operation, equipment failures can be predicted and consequently avoided. Siemens’ use of artificial intelligence in its approach to predictive maintenance proves that data analysis helps improve manufacturing.
Quality Control at BMW
BMW, a highly recognized automobile company, is using AI to improve quality assurance programs. Applying AI technologies in the production of vehicles guarantees that every manufactured car is of high quality and safe to use.
AI applications at BMW include computer vision systems to check the physical structure of cars. These systems employ intelligent image analysis algorithms to recognize defects and variability during production. This means that BMW identifies and corrects the problems before defective products are taken to market. This helps in increasing the quality of the products and also decreases the waste and costs associated with reworking.
The main lesson that can be learned from BMW is that the implementation of artificial intelligence in quality control is fast and accurate. AI technologies are effective when it comes to inspections because they can deliver results that are more precise and standardized than a human can offer. This is important in increasing organizational productivity by ascertaining that there is steady compliance with high quality in delivery, thereby increasing the quality of the brand and customer satisfaction.
Also read: Best AI in Software Development Use Cases for 2024
V. Challenges of AI in Manufacturing
Generally, AI in manufacturing has its advantages, but its use is accompanied by several barriers that should be overcome by the manufacturers for the concept to reap the intended benefits. These include technological encouragement, data management, and changes that affect the organization’s employees. Here, the paper outlines the main difficulties related to AI integration into the manufacturing sector and ways for their resolution.
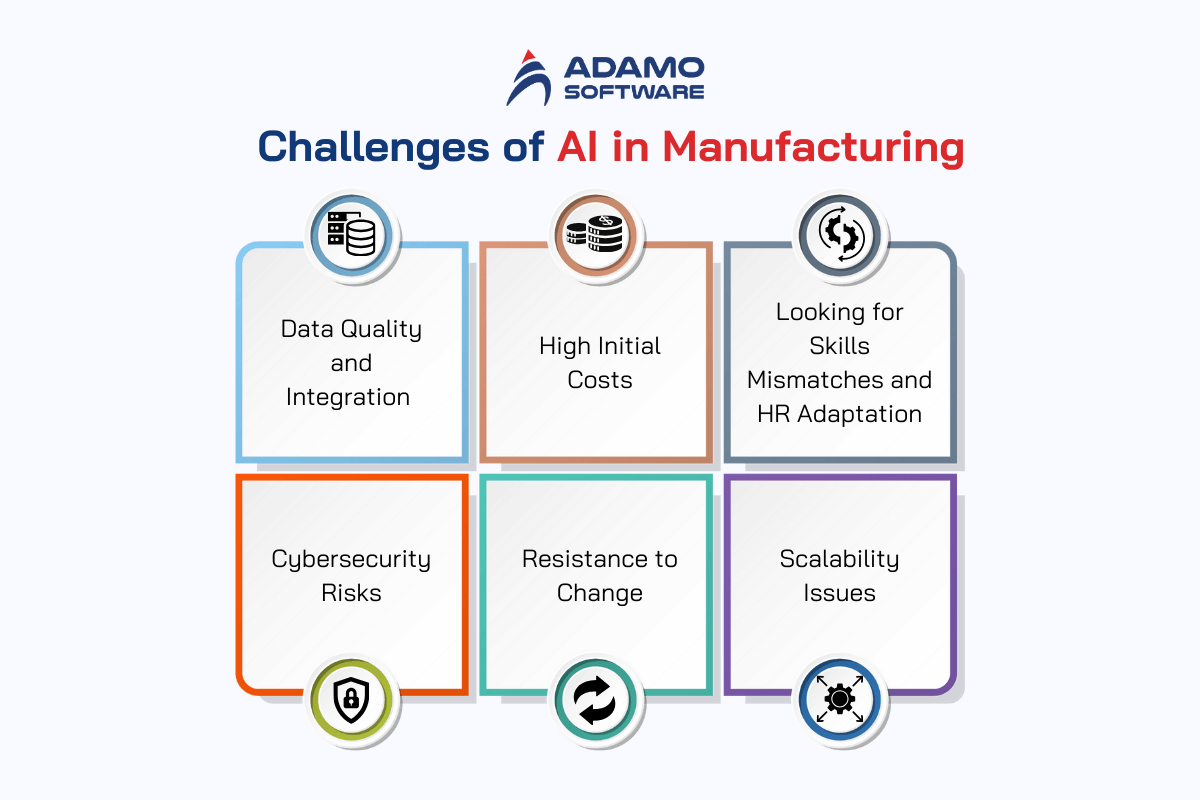
1. Data Quality and Integration
Challenge: The biggest challenge in the application of AI in manufacturing is how to obtain good-quality data. AI systems, as we have seen, depend on a large amount of data to work, while manufacturing scenarios are faced with heterogeneously diverse data sources, consequently resulting in unpredictable datasets.
Solution: To address this, manufacturers should focus on collecting and integrating quality and reliable data. Using standard procedures for data handling and dispersion, as well as progressive data cleansing and preprocessing instruments, can improve the quality of the data considerably. Also, by implementing IoT devices and sensors, it is possible to source more consistent and accurate data.
2. High Initial Costs
Challenge: Firstly, there is a direct cost involved in implementing AI in manufacturing firms, and most of these costs are capital intensive. Such costs are not only restricted to the cost of the software and the machinery that go into the deployment of the AI but also the costs that accompany it, such as training costs and other costs.
Solution: There is a way through which manufacturers can be able to contain these costs; this can be achieved by manufacturers adopting pilot projects that have a very clear performance, especially concerning ROI. They also include partnering with AI vendors that have more flexible pricing structures or applying for government loans and subsidies to offset the costs. Also, fewer investments would be required for the basic infrastructural setup if cloud-based AI solutions are employed.
3. Looking for Skills Mismatches and HR Adaptation
Challenge: The use of AI in manufacturing means that the workforce is in a position where it has to learn certain new skills. However, there is always a skills chart that indicates that while existing employees are great, they do not possess the knowledge required to work on or with AI.
Solution: Learning, development, and experience management must be a priority for an organization’s management. Manufacturers should also look at collaborating with schools and colleges to attempt special course development. The encouragement of continuous learning while working and upgrading within the organization can also help to ease the process.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
Challenge: AI system implementation in manufacturing leads to the augmentation of cybersecurity challenges. Cybersecurity threats are also a challenge for AI systems because the system may be targeted for cyber-attacks which may eventually disable the system and also steal data from the users.
Solution: The book under discussion proves the necessity of the proper use of cybersecurity measures. This entails incorporating new forms of encryption, frequent security scans, and integration of automated artificial intelligence security that helps recognize and actively counter emerging threats. Manufacturers also need to set policies regarding how the data is to be managed and who has the right to access it.
5. Resistance to Change
Challenge: Lack of change mentality is one of the factors that contribute to the slow integration of new technologies. Enterprise employees or managers may not see the advantages of AI technology or may worry about being replaced by machines.
Solution: Such change management is way too important Importantly, one needs to distinguish between change management and change leadership. Education, including informing people about the advantages of using AI in manufacturing in the long term, including employees, and showing how others have been successful in using AI can help. Ambiguity reduction concerning job security and the focus on how AI complements human work instead of replacing it can receive credit for this.
6. Scalability Issues
Challenge: The transition of applying Artificial Intelligence from the initial stage, where just some projects are applied, to a large-scale application can be difficult. Implementing those strategies that have been successful in a more limited sphere may thus present problems on the scale of an entire manufacturing undertaking.
Solution: It is also important for manufacturers to proceed step by step during AI implementation, which means the application of this technology should be gradually expanded. The conduct of tests and validation on the various facets of each phase will aid in the identification of problems that can be solved before progressing to the next phase. Another aspect is that interacting with experienced AI solution partners can help with easier scaling.
VI. Final Thoughts
It is no longer a trend but a revolution to integrate AI in manufacturing. AI technologies drive efficiency improvements, supply chain management, as well as the introduction of innovation. Producers embracing the above technologies are ensuring that the upcoming future of production is more uncertain and positive. Adamo, for instance, is one of the companies leading in AI solutions and is at the center of this revolution.

On the positive side, when applied to manufacturing, AI creates new possibilities for functions like predicting failures in equipment and ensuring quality control and supply chain management. It also elevates the sustainability of the environment through purposes of downtime, waste, and energy. Also, AI in manufacturing helps with mass customization which is a rapidly growing trend. Adamo’s experience shows that companies can adopt AI into their processes without sacrificing any advancements and can develop a gleaming future for manufacturing.