How to Implement Healthcare Data Warehouse: Benefits, Architect, Cost

Are you managing your clinic – not just any kind of clinic but a very active one? We bet you have patients coming in one after the other, all with their different medical histories. But that history is stored in different drawers of filing cabinets, in various programs on the computer, and on pieces of paper where someone jotted down some information! Searching for information sometimes appears more challenging than searching for a particular grain of sand on a beach full of it.
This data overload is a real issue in healthcare. But don’t worry! There is a solution though, and it is a healthcare data warehouse. It is like a large cabinet where all the documents regarding a particular patient are kept and well arranged. Sounds pretty sweet, right?
In this article, we will focus on all aspects of healthcare data warehouses. We will define what they are, how they may be helpful for the hospitals and clinics, and how there are variants of how to implement one. We’ll even discuss here a little bit about the cost, which, you know, is important to most of us! By the end, you will be in a better position to determine whether a data warehouse is the solution to the health facilities working more efficiently and ensuring better patient care.
I. What is Data Warehouse in Healthcare
Suppose your hospital is like a city where people are flowing in and out constantly. Data circulates at every step – patient records, lab reports or even the data from the fitness trackers! But this data is dispersed into different filing cabinets, and it is hard, if not impossible to locate something.
Meet your lifesaver: healthcare data warehouse. This concept is like the healthcare industry is one enormous warehouse with complex shelving systems for storing all kinds of data. It extracts data from EHRs, lab results, and even wearables and consolidates all of the data in one central location, which is secure.
But wait a minute, this is only a part of the puzzle. There’s a whole process that is simply like a data conveyor belt – data is received, processed and then provided to the end user in a format that is understandable.
II. How the Healthcare Data Warehouse Works
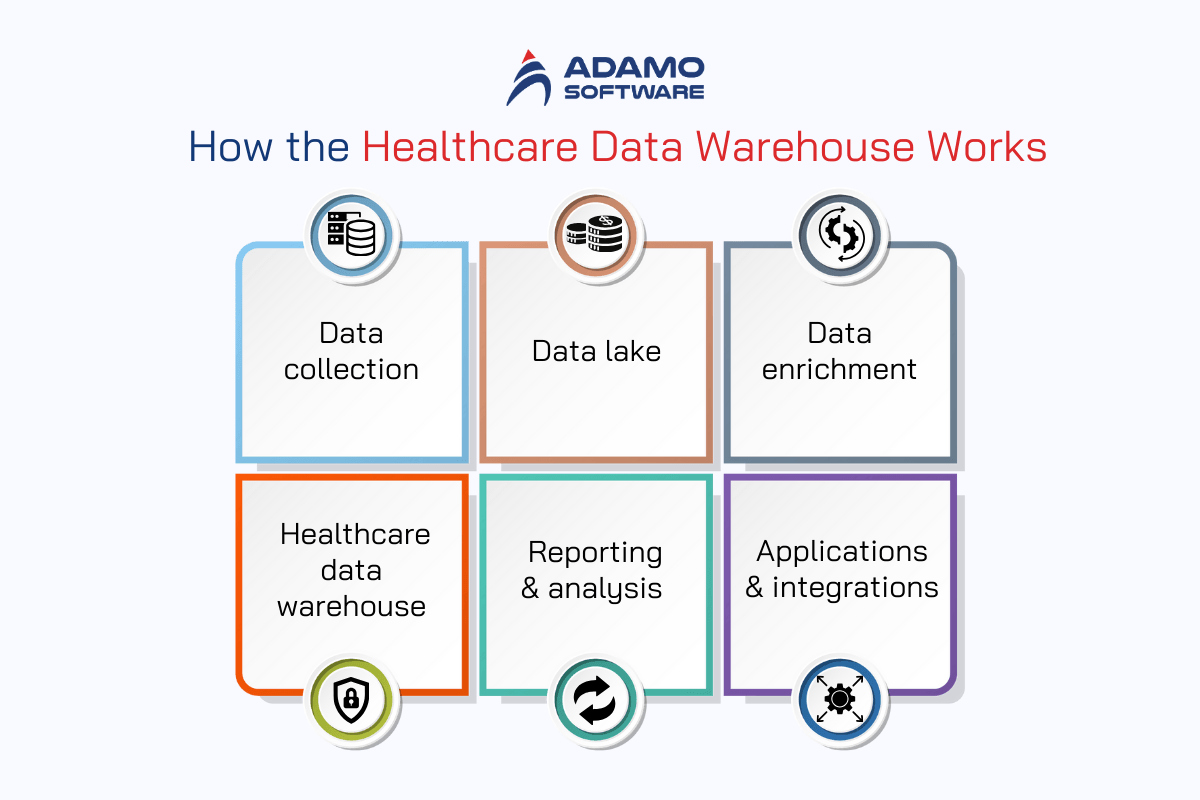
1. Data collection:
Think that many trucks are collecting information from all the corners of the hospital city. It determines what data is important and then goes out to fetch it, this is known as the connectivity layer.
2. Data lake:
This is a huge receptacle where all the raw, unstructured information is kept. It is like a big pile of toys before the child categorizes them into different groups.
3. Data enrichment:
Here’s where the magic happens. Special software cleans up the data lake, making sense of all that information and turning it into something usable.
4. Healthcare data warehouse
The organized data is then transferred to the healthcare data warehouse section. This is like a supermarket that has all the commodities one needs; it is even better since it is online.
5. Reporting & analysis:
It can help analysts and doctors to build reports and dashboards based on the patient data which will be useful in analyzing patient care, trends, etc.
6. Applications & integrations:
It is possible to consider these as specific instruments that can be developed based on the information stored in the healthcare data warehouse. Think about a gourmet restaurant preparing meals with the finest ingredients, which, in this case, are the data!
It’s important to keep the data lake and the healthcare data warehouse separate. The data lake is like a messy draft, while the healthcare data warehouse is the final, polished version. If you mix them up, it’s like trying to cook with a pile of random ingredients – the results won’t be pretty!
Building a good healthcare data warehouse takes some effort, but the benefits are totally worth it. In the next section, we’ll dive into how a data warehouse can revolutionize the way you deliver care!
III. Benefits of Leveraging Healthcare Data Warehouse
A healthcare data warehouse can be viewed as a chest full of healthcare data properly sorted and classified. It collects data from various sources such as the test results, patients’ records, including the EHRs, and insurance claims. This enables the doctor to have a holistic view of the patient and therefore make good decisions that benefit the patient.
Here’s how a healthcare data warehouse can offer clinics so many benefits:
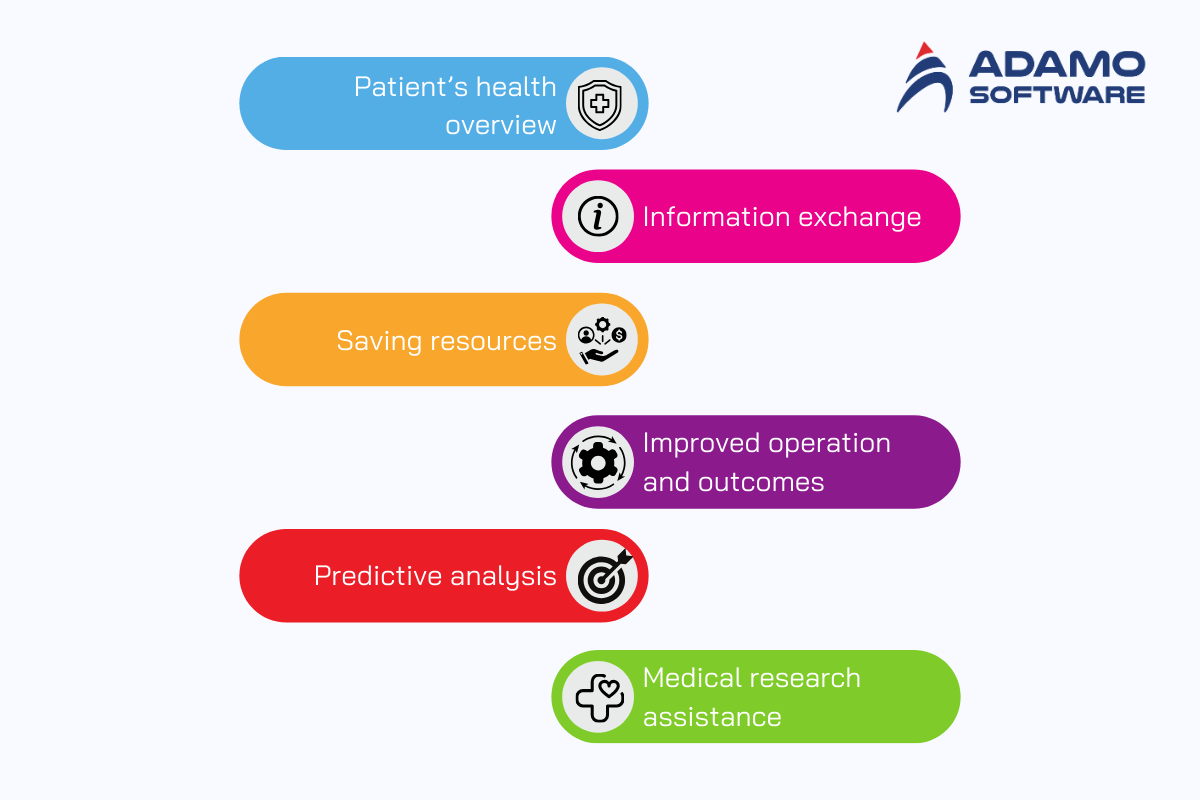
1. Patient’s health overview
Say goodbye to days and nights of assembling a patient’s health history by sorting through bits of paper on their chart. The healthcare data warehouse pulls all of it together and presents it to the doctors so they can have a full understanding of the patient.
2. Information exchange
The healthcare data warehouse contains information on patients, and doctors, nurses, and other health care givers – pretty much everyone within your healthcare system can have access to the information. This promotes a better integrated machine in the provision of health care services, given that the various players are in harmony.
3. Saving resources
Have you tried looking for a particular document in the room that has just been cleaned up and in the cluttered one? It must’ve felt really frustrating! Healthcare data warehouse eliminates time spent in searching for information, meaning that the important aspect of the healthcare provision, namely patients, receives the attention they deserve.
4. Improved operation and outcomes
Since all the data is easily accessible, doctors can look at trends and see potential problems faster. This is because it enhances the rate at which diagnoses can be made and subsequently, treatments.
5. Predictive analysis
Healthcare data warehouse is a health care crystal ball. An extensive amount of data can be processed to predict the occurrence of the disease, the patient population at risk, and even discover new treatments.
6. Medical research assistance
Researchers can use the healthcare data warehouse to access a wealth of clean, organized data. This helps them uncover new insights into diseases, develop better treatments, and ultimately, improve overall healthcare.
Of course, creating a healthcare data warehouse is not a piece of cake, literally. It calls for capital and skills. However, the advantages that can be obtained are far beyond the difficulties that can be encountered at this stage. The healthcare data warehouse represents a treasure of data if only it will be used effectively. That means improving patient care, the health of all people, and the management of healthcare organizations.
You can explore What is Health Data Management? Benefits, Challenges and HDM Software here.
IV. Healthcare Data Warehouse Architecture
Healthcare data warehouse is more of a blueprint that outlines how to create the health care system’s brain. This blueprint outlines how the design of your data warehouse will be done based on your hospital’s size, your objectives and the specialized area that you operate in. There are two fundamental architectural styles that are possible, and selection between them is crucial for the efficient work of the brain (which is for data analysis in this case).
1. Individual data warehouses
This may be viewed as a mini brain that specializes in a certain area of the body, for example a pharmacy or a radiology section. It contains information relevant to that specific department. This enables medical staff to run analyses of the rates of certain illnesses or employing certain equipment. This is ideal for small hospitals or for those which wish to address certain issues in a short amount of time.
Here follows the great thing: these mini brains can develop! They can begin with a simple problem that requires the analysis of a single source of data and expand to serve more data when necessary. However, they do not have full access to the hospital’s information base, which can be considered disadvantageous.
2. Enterprise data warehouses (EDW)
This is the ultimate data repository that contains data from virtually every part of the hospital – be it EHR system, pharmacy database or patient feedback. It’s like a big brain with different lobes, each of which deals with different types of information.
Here’s how the EDW brain works:
- Data source layer: You can think of this as all the information sources in the hospital – EHRs, lab results, insurance claims – act kinda like the body’s sensory organs.
- Staging layer: This is like a reception area where the data is arranged and prepared before it gets into the actual processing center. All the information is put in the same format, and any information that has been repeated is removed.
- Data storage layer: This is the working or the operational part, the depot, the central memory, as it were, of the organ. Here, clean structured data is kept waiting to be analyzed since it is a data warehouse. It can also contain mini-brains or data marts for individual departments of the organization.
- Data reporting and analytics layer: This is the part where the thinking happens! Some of the ways doctors and researchers can use the data collected include analysis to discover patterns and trends and help in decision making. From simple things like fancy charts and graphs to the more advanced techniques such as machine learning, they can all find meanings from the data.
This work also reveals that, while the process of constructing an EDW is not simple, the advantages that it offers are truly fantastic. It is the process of enhancing the ability of your hospital by endowing it with a superior brain. This “brain” helps to diagnose the diseases and treat them more effectively to make the future of people healthy.
V. Data Warehouse Healthcare Use Cases
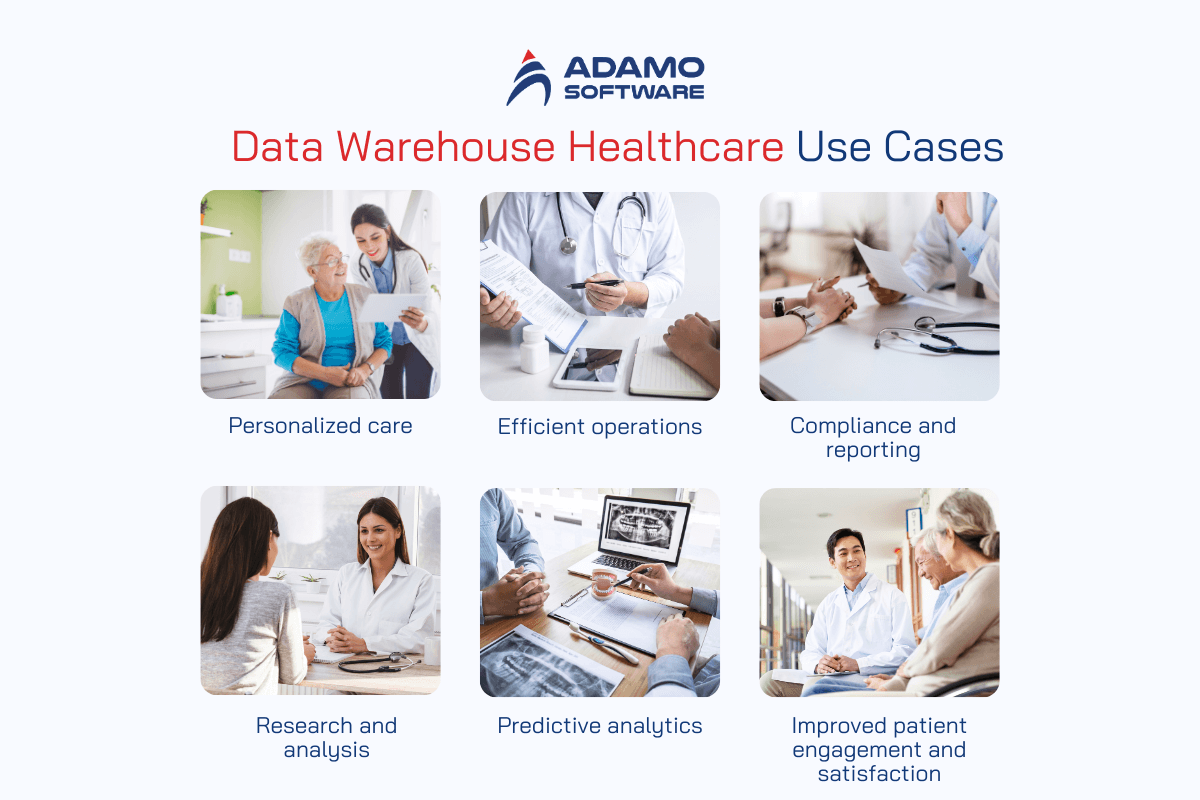
1. Personalized care
Patient data scattered in various systems hinders the delivery of appropriate patient care. Thus, healthcare data warehouse fills this void by bringing together data and offering a complete picture of a patient’s clinical record. These three different levels of patient data can be combined to give doctors a complete picture of a patient. From there, subsequent suitable treatment can be developed, increasing the chances of positive patient outcomes.
Technical implementation:
- ETL processes: Data cleaning and organization is done before data gets into the warehouse through ETL. This makes the information within the healthcare data warehouse accurate and consistent.
- Data integration: Information from different systems is compiled and transformed into a single and accurate database of the patient.
2. Efficient operations
Fragmented data in the areas such as scheduling and supply chain results in elevated operational costs. This is where healthcare data warehouse comes to the rescue, which compiles all operative data. This makes it possible to evaluate the use of resources and the execution of activities and procurement and distribution of products and services. Inefficiencies should therefore be actively sought out for the healthcare organizations to seek ways of making the processes more efficient and thus more economical.
Technical implementation – Analytical tools: These tools provide information and reveal sectors that require more attention as far as resource consumption and processes organization is concerned. In this way, the healthcare organizations can proceed with data analysis to enable them to make the best decisions that will enhance operation.
3. Compliance and reporting
Manual reporting of compliance is inefficient, inaccurate and can attract a penalty. Healthcare data warehouse is keen on the accuracy and consistency of the data they store, in addition to satisfying legal necessities. Relevant data is collected and preprocessed automatically while the format must comply with the set of regulations. This eases the reporting process and reduces the occurrence of mistakes.
Technical implementation:
- Data consistency: Some common steps followed to ensure the credibility of data in the data warehouse include data validation and cleansing. Compliance reports are credible if the data on which they are based is trustworthy.
- Reporting tools: BI tools are also used for report automation and guarantee the observance of the requirements set by the regulating authorities. These tools provide a way of automating the formatting and the scheduling of reports, hence, minimizing the amount of work to be done by hand.
4. Research and analysis
While the data consist of various formats and are derived from different sources, it becomes challenging to analyze the treatment results and perform clinical research. Healthcare data warehouse compiles clinical data from several studies and trials, normalizing them for use and analysis. Considering the obtained results, it is possible to analyze trends with the help of a single dataset. Doctors can then evaluate treatment effectiveness and develop new medical hypotheses for further research.
Technical implementation:
- Data standardization: This deals with data formats and terminologies used in the clinical datasets. These are guaranteed to be made consistent to ensure that the datasets can be easily analyzed.
- Analytics platforms: Different levels of analytics are used to analyze data and present the research outcomes in visuals. Such platforms enable one to find patterns and relationships that one may not notice through structured analysis.
5. Predictive analytics
Controlling sickness incidences and avoiding persistent conditions cannot be predicted without concrete data processing tools. A wide range of data types, such as patients’ records and data from wearable devices can also be integrated at an advanced level through cloud data warehouses. For example, data scientists can use statistical analysis to find vulnerable groups, predict diseases’ occurrence, and avoid their spread.
Technical implementation:
- Data integration: Electronic records from hospitals, health departments, and fitness devices provide a detailed analysis of a patient’s health status.
- Predictive models: Machine learning techniques are created and used for data analysis and for making the prognosis of diseases. This makes it possible to prevent risky conditions from arising to harm the population’s health.
6. Improved patient engagement and satisfaction
In cohesive models, patients’ needs and preferences cannot be defined, which lowers satisfaction. Patient interactions data include treatment history, appointments, channels of communication, feedback forms, and are stored in cloud data warehouses. Such an approach helps in creating specific interaction and related communication tactics, which contribute to enhancing patient satisfaction.
Technical implementation – Engagement tools: Patient engagement tools are used to communicate with patients, with the primary motivation being the data warehouse analysis. They can be used for sending reminders for appointments, health tips and feedback daily for improvement.
VI. How to Implement Data Warehouse in Healthcare Industry
The potential of applying knowledge in healthcare data warehouse is vast. It allows for enhancing the care of patient’s increasing efficiency and promoting the advancement of research. Nevertheless, the construction of one demand great and sound planning and design. Here’s a detailed roadmap to guide you through each crucial step:
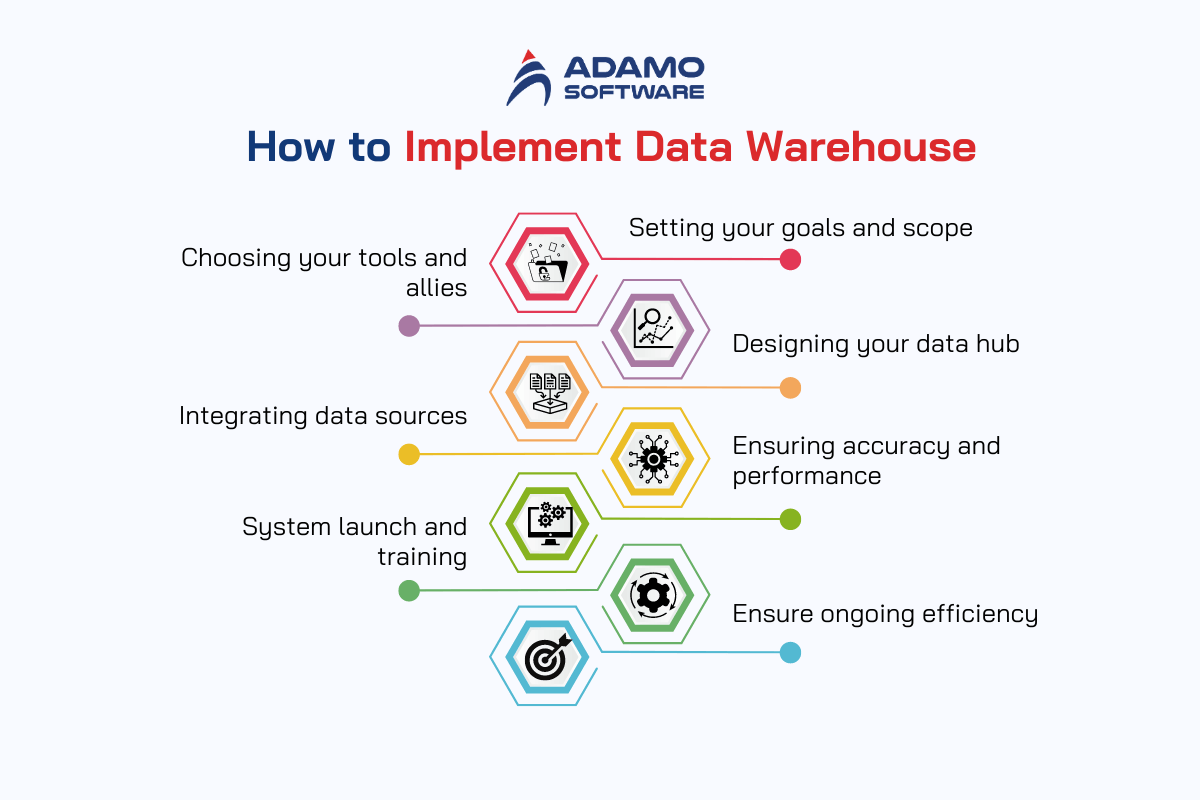
1. Setting your goals and scope
The goals and scope of an individual may be different from that of the organization. So, the first step of this process is identifying the goals and scope at the management level of an organization.
Thus, the journey starts with establishing the goal. It is thus important to clearly state the goals expected with the data warehouse. This involves determining special requirements for handling healthcare information. It could be about improving health results by customizing treatment regimens or increasing productivity from processes within the healthcare facility. Then, describe where your project will be focused based on the data sources you have planned on consolidating, the amount of data you will process and the KPI you’ll use to assess the outcomes. The implementation of a clear vision and measurable goals will help in decision making as you proceed with the process.
2. Choosing your tools and allies
The infrastructure you choose will be your foundation for the healthcare data warehouse system. This involves selecting the right databases for dealing with a variety of needs of healthcare data. It further includes the ETL tools for extracting, transforming and loading the data into the right format and data warehousing. Analytics tools for data extraction are also a part of the consideration. Don’t go alone! Consulting with those technology suppliers and consultants who have vast experience in healthcare data warehousing can be of great help. They have practical and theoretical expertise that allows them to deal with technical issues. This helps ensure that the selected approaches wouldn’t negate the main objectives.
3. Designing your data hub
The process of constructing a healthcare data warehouse is as similar as designing the route map of the information center of your healthcare organization. It describes how and when data will be gathered, stored, and processed. This entails creating a system that will be able to meet your requirements. You will opt for how you wish to store the data, how you will preprocess and transfer the data and how you will configure tools that will help you find important information. The careful planning of such architecture guarantees that your data warehouse is optimally functioning and meeting your organization’s data needs.
4. Integrating data sources
The healthcare data warehouse depends on the information contained within it for its strength. This is the place where you will be consolidating information from different sources, within a healthcare organization. This may comprise Electronic Health Record systems (EHRs), Billing systems and Patient Management systems. Incorporating all these various sources involves having processes for data scrubbing and data verification. Quality and data consistency are important for deriving meaningful insights and making proper decisions.
5. Ensuring accuracy and performance
Just like any complex system, your healthcare data warehouse needs thorough testing to guarantee its functionality and performance. This involves carrying out extensive checks and tests to confirm that the system’s behavior is as expected. It also checks for accurate reflection of the integrated data and meeting the predetermined performance benchmarks. If the performance of the system is compared with the initial set of KPIs, one can determine the existing issues or changes necessary. This ensures that the healthcare data warehouse that you design meets the intended objectives and is optimally designed for managing the flow of data.
6. System launch and training
When you are sure that the system is ready, you can proceed to launch it. Use the data warehouse throughout your healthcare organization with the correct interfacing of other systems. It is for this reason that sufficient training needs to be provided to the staff and the users of the system. Developing the users’ competence and knowledge enables them to exploit the data warehouse optimally in supporting decision making and ultimately in delivering quality patient care.
7. Ensure ongoing efficiency
Your healthcare data warehouse is not static. They must be updated often and maintained to remain useful in the constantly evolving healthcare industry. This means change regarding new technological and data practices. Maintenance is also crucial as well as enhancing and repairing bugs and other problems that may hinder the software from working. Thus, the data warehouse only gets better and better. It also becomes valuable and reliable in the constantly changing landscape of healthcare data. This in turn helps to improve patient care.
VII. Cost of Healthcare Data Warehouse
Building a healthcare data warehouse can cost anywhere between $70,000 and $1M depending on the size and complexity of the project. This generally takes about between three to twelve months.
The cost can be different based on the size of your organization. For example:
- 200 – 500 employees: $70,000-$200,000.
- 500 – 1000 employees: $200,000 and $400,000
- 1000+ employees: Up to $1,000,000.
It is also important to note that these estimates don’t include ongoing software fees.
VIII. Adamo Provide Professional Development Service for Healthcare Data Warehouse

If in doubt, let Adamo Software help you to implement your healthcare data warehouse. After years, we excel at Remote Patient Monitor, Wearable Devices, Telemedicine and on-demand healthcare solutions to transform healthcare services innovatively.
We specialize in technological solutions for many different sectors, including the healthcare software development industry. Our team of experts will help you find the best option to level up your medical center with cost-effective and high-quality service.
Contact us to discuss more about how we can assist you!





