Healthcare CRM software: Features, tech stack and how to implement

A successful working relationship between healthcare professionals and patients is crucial in transforming patient care. This is where CRM software for healthcare proves itself. Contrary to typical database systems, this software assists organizations in addressing patient issues. It enhances communication and provides services with a more individual character.
Selecting the right CRM software for healthcare is not about making the right tool choice; it is about the right match for the practices. A custom solution is more intelligent because of the flexibility that comes with it plus the integration it has with your processes. Hence, by incorporating key features such as appointment reminders, reporting, and messaging platforms, you could offer a higher quality of care with increased profitability.
In this article, you will learn how to shape CRM software for healthcare by revealing the features that should be implemented, the issues that need to be avoided, and practical steps for building them.
I. Why should choose custom healthcare CRM software over traditional
Custom CRM software for healthcare is more suitable for healthcare organizations than the mainstream system, as the former is shaped. While conventional CRM tools are broad and standardized, the CRM systems developed for specific companies are tailored to processes. This makes them handle patient relations better and more personalized.
The best part is that individual CRM software for healthcare will enable the incorporation of core elements. Those can be appointment setting options, patient communication instruments, and data protection services. It is a more sophisticated system because, compared to other conventional systems, it is very flexible. It can allow for the incorporation of other functions if the organizational structure changes. It even expands processes if the organization expands. This means that the software will continually be updated to suit the business.
Custom-built CRM software for healthcare also offers better compliance with regulatory laws in the healthcare industry, including the Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act (HIPAA). Given that such requirements have been captured while developing the application, it guarantees patient record security and patient information privacy. Besides, it can easily link with other healthcare equipment, such as EHR, which makes the workflow easier.
In conclusion, opting for customization of CRM software for healthcare includes proper solutions, compliance, and scalability. It frees healthcare providers ‘time and attention up so they can concentrate on what counts—improving patient bonds and service delivery. Because of the above-discussed factors, the custom CRM software for healthcare options is even smarter than conventional CRM.
II. Essential features to include in your Healthcare CRM software
To build effective CRM software for healthcare, it’s important to include features that address the needs of patients and healthcare providers. These features help streamline operations, improve patient relationships, and ensure regulatory compliance. Below are the essential features:
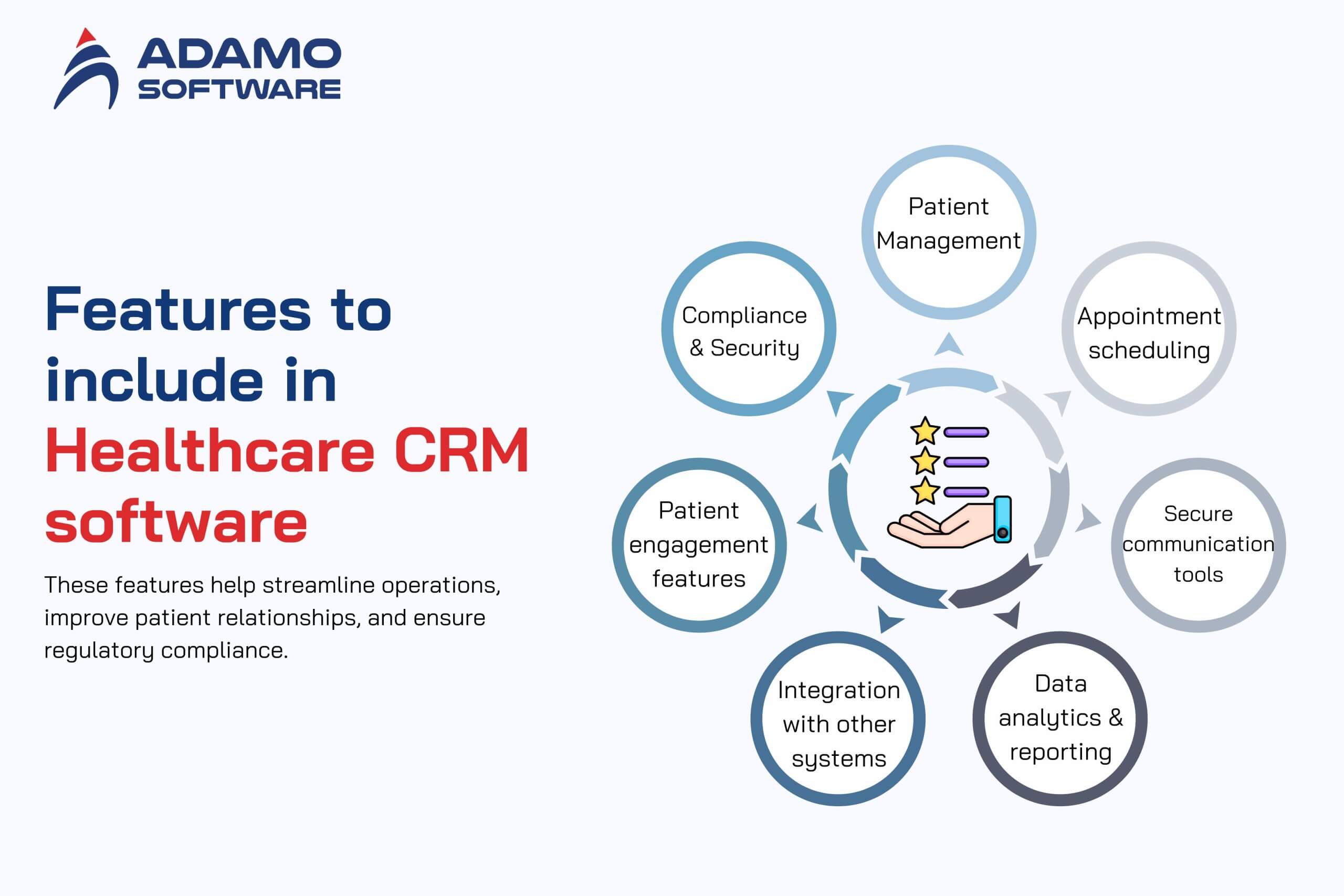
1. Patient Management
- Centralize all patient data, including personal details, medical history, treatment plans, allergies, and test results.
- Offer easy search and filter options for providers to access patient information quickly during appointments.
- Enable providers to track a patient’s progress and coordinate care across teams.
2. Appointment Scheduling
- Allow patients to book, reschedule, or cancel appointments online without contacting staff directly.
- Include a calendar view for staff to manage appointments efficiently and reduce scheduling conflicts.
- Integrate automated reminders via email or SMS to reduce missed appointments.
3. Secure Communication Tools
- Provide encrypted messaging systems for patients to consult with their providers securely.
- Offer video conferencing for telehealth services, ensuring high-quality interactions while maintaining privacy.
- Enable real-time notifications for updates on test results or prescriptions.
4. Data Analytics and Reporting
- Include dashboards that provide insights into patient demographics, service usage, and outcomes.
- Enable providers to analyze appointment trends, identify frequent no-shows, and optimize scheduling.
- Offer custom reporting tools to help healthcare organizations meet internal goals and comply with regulatory audits.
5. Integration with Other Systems
- Ensure seamless integration with electronic health records (EHR) to sync patient data in real-time.
- Connect with billing and insurance systems to streamline payment processes and reduce administrative burden.
- Integrate with marketing tools to manage patient outreach programs effectively.
You can explore more about Hospital Management Systems: Types, Key Features & Must-Know Insights here.
6. Patient Engagement Features
- Make client appointment reminders for their next appointment, refill prescriptions, and the next follow-up checkup.
- Share informative food or health promotion messages to interest the patients.
- Know the patient’s concerns. The satisfaction survey must be included and ensure the patient’s comfort and rights are protected.
- Also, check the system is HIPAA and GDPR-compliant to address the issue of client confidentiality.
- Avoid unauthorized access using MFA and data encryption.
- Security should be updated periodically to counter the new challenges posed by cybersecurity.
- Send personalized wellness content, such as diet plans or preventive care tips, to keep patients engaged.
- Include satisfaction surveys to gather feedback and improve the patient experience.
7. Compliance and Security
- Ensure the system complies with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to protect sensitive data.
- Include multi-factor authentication and data encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
- Security protocol updates to address emerging cybersecurity threats.
When implemented, the features make CRM software for healthcare more effective in healthcare delivery, patient satisfaction, and organizational efficiency. Such functionalities enable providers to deliver differentiated, speedy, secure healthcare services.
III. Steps to build the best healthcare CRM systems
Developing a robust method for implementing CRM software for healthcare could also be challenging. All the steps are valuable in achieving a system that would facilitate both the provider and the patient. Here are the steps involved in creating the best CRM software for healthcare outlined as follows:
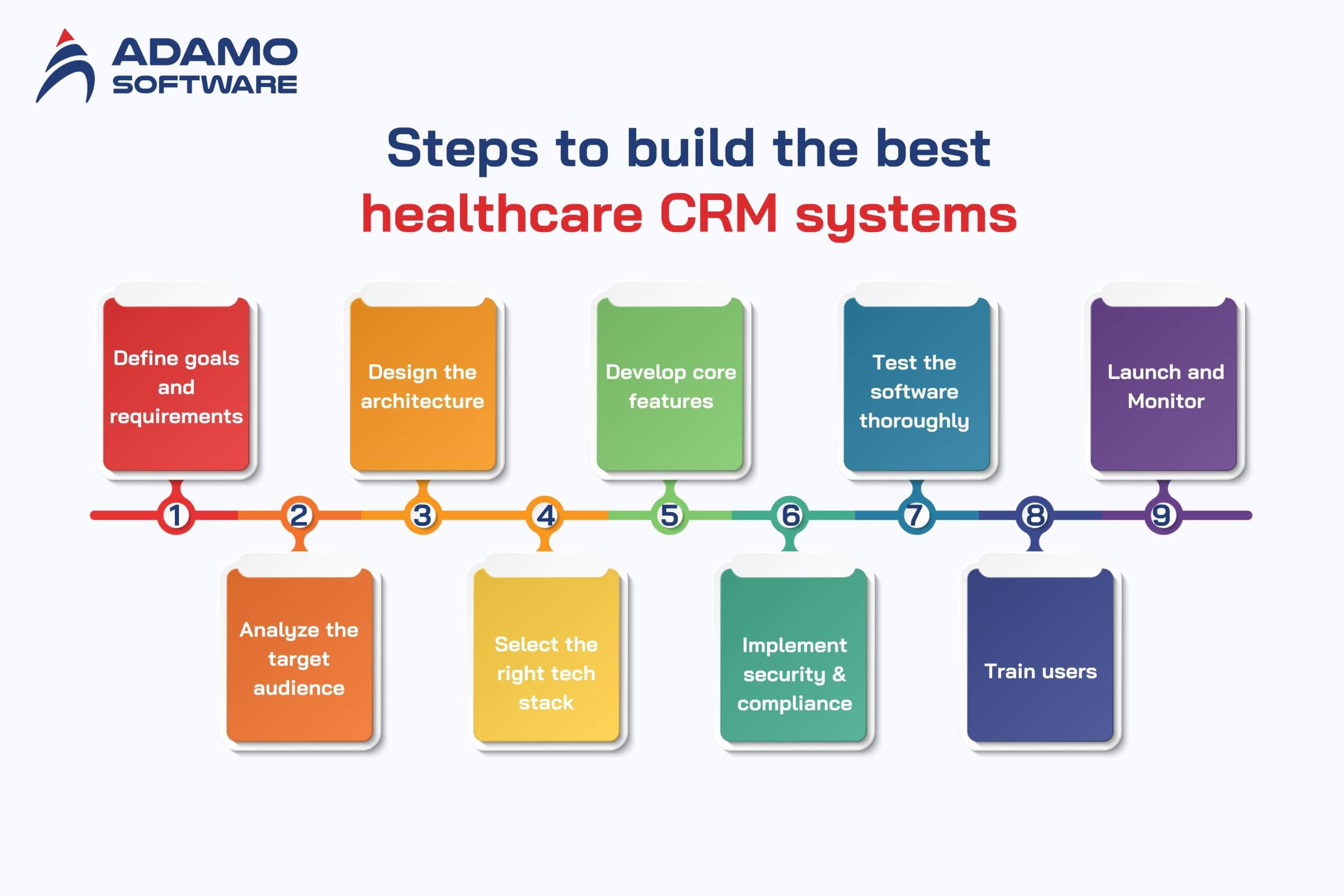
Step 1: Define Goals and Requirements
To establish the objectives software will have to meet, let’s start with the four major ones for healthcare CRM. Identify what your organization would like to accomplish. For instance, increasing the patients’ satisfaction, integration of schedules, and data security, among others. Sit down with the healthcare provider, the administrative staff, and the information technology department to prepare a list of emergencies that are mandatory.
This guarantees that the software is in a position to solve certain organizational problems and will adhere to some organizational workflows. About the above, it is important to be clear on what is expected to be accomplished during the project. You must exclude aspects that are likely to complicate the project’s development.
Step 2: Analyze the Target Audience
Assess the demands of the users that will utilize interaction with the CRM software for healthcare. Some patients may need simple features such as booking an appointment, communicating securely with the provider, and receiving reminders. Other providers may require features that allow extracting and analyzing patient data and generating reports among others.
Take time to ensure that the interfaces are friendly and anyone with little knowledge of the software system can easily use the system. Ask the patients or employees questions so that you can establish what they would like to see changed in a facility or hospital, or what complaints they may have.
Step 3: Design the Architecture
Design a road map on how the CRM software for healthcare will work. Product plan: the system elements, the patient record, analytic sub-modules, the communications channels, and interfaces to electronic health records (EHRs). Ensure that design fundamentals consider the architecture of the effort to grow proportionately with the scope and size of the businesses. If you’re betting on more expectant years, then the priority is to start with a modular construction. Since in the future, chances are high that you will be requiring more feat.
Step 4: Select the Right Tech Stack
We should settle for systems that suit the project’s needs in all aspects. For the back end, possibilities such as Python or Node.js and Ruby on Rails ensure versatility and solidity. In this case, frontend frameworks such as React or Angular assist in developing a best-performing interface. Ensure the tech stack is compatible with enhanced security measures and protocols such as data encryption and multi-factor authentication for healthcare data.
Step 5: Develop Core Features
When interacting with software development, carefully pick important features for CRM software for healthcare.
- Deriving elements such as patient management for storing and retrieving patient information.
- Appointment scheduling, such as time scheduling, to remove unfilled appointments in an instance time frame.
- Protect communication techniques, including encrypted messages and video conferencing, among others.
- Patient tracking and data analysis to help the clinic understand certain aspects and performance of the organization.
Ensure the design includes scalable architecture so the system can grow alongside your organization’s needs. Focus on building a modular structure, which makes it easier to add features or make updates in the future.
Step 6: Implement Security and Compliance
Security is important in handling health care information. For instance, let your CRM software for healthcare be HIPAA and GDPR-compliant by adopting items like data encryption, proper login, restrictions, and others. Ensure you update the software periodically to meet the ever-changing law compliance and ward off new risky threats.
Step 7: Test the Software Thoroughly
Testing is important to determine how the software will work in the real environment. That is why you need to test the system’s capabilities; it is necessary to create situations where a large amount of data or several users are processed. Get feedback from some test users, the staff, and the patients to discover the different difficulties in the usability designs.
Step 8: Train Users
Ensure that all the staff are trained by giving them sessions that will help them understand the new system. Design handbooks and videos as well as informative and engaging learning exercises. Ensure that it answers ordinary questions and fosters questions to increase the user’s confidence level. Training also enables people to transition smoothly, knowing how to conduct their work with the software.
Step 9: Launch and Monitor
Implement the CRM software for healthcare in stages to start with a limited number of people and to see how effectively it works. This is beneficial in making changes where necessary before a company goes ahead and launches a product on the market. Fixed procedures should then be followed to check the performance, security, and how this system is scaled. Continuous updates of the software and feedback from the users will assist in the management noting any changes and improvements.
With the above steps, one can be in a position to design effective, user-friendly CRM software for healthcare that will help to protect the patient’s information. This creates happy customers and the health facility on the provider end while at the same time increasing the effectiveness of operations.
IV. Challenges when developing Healthcare CRM software
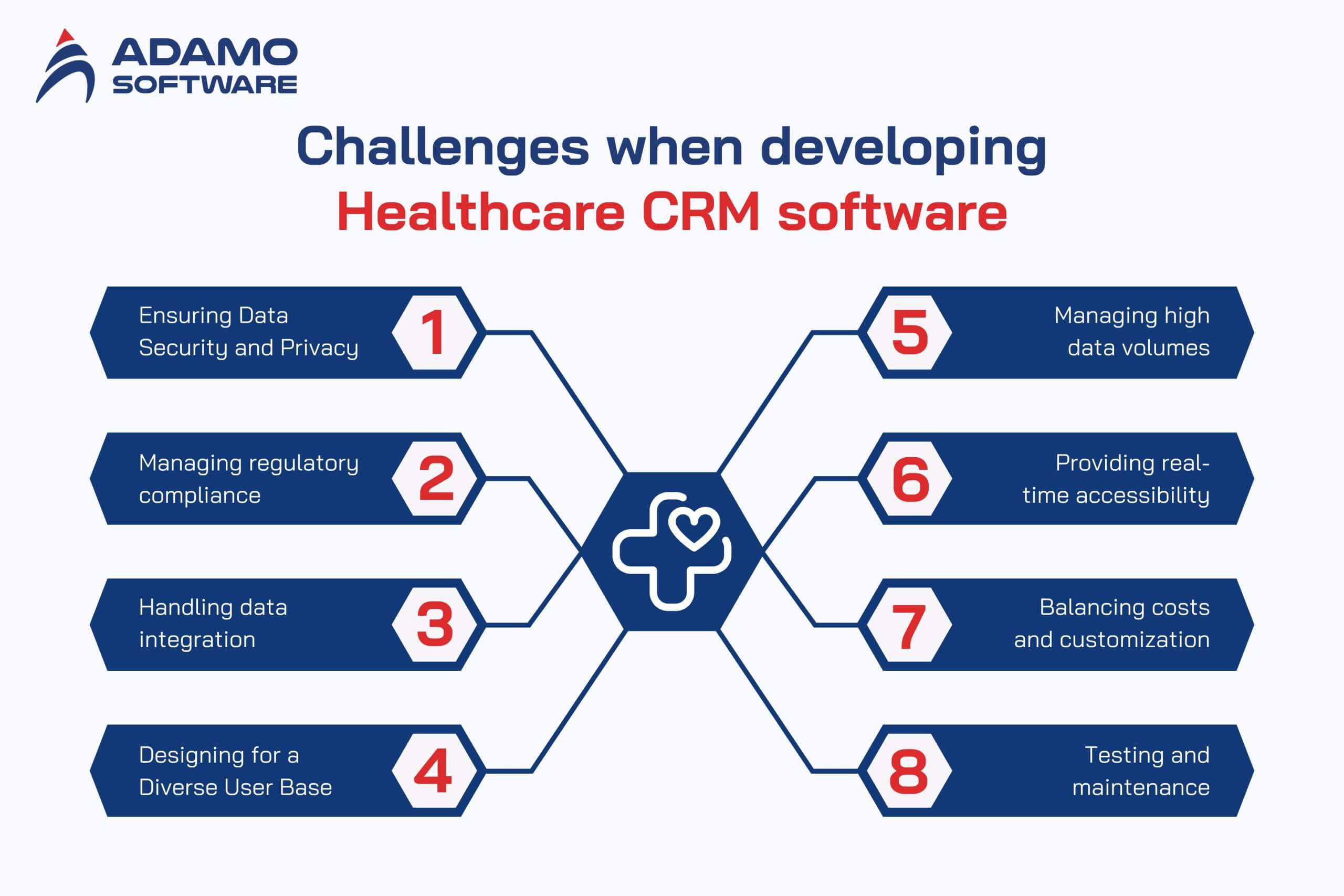
Healthcare CRM software development can be a very daunting task that presents some forms of challenges. These issues derive from the fact that healthcare data is often confidential, users vary greatly and are many. There are also many regulatory requirements in the healthcare industry. Here are the main obstacles developers may face when creating CRM software for healthcare:
1. Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
A significant challenge of creating CRM software for healthcare is data security: patients’ data are always sensitive. To accommodate ‘claims of personal health information’, the software must meet regulatory standards such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in the European region. Security measures needed with the use of data developers include encryption of information, user authentication, and security access. It is dangerous to offend or compromise the security of a nation, a company, or an individual. Since it attracts stiff penalties and loss of dignity and confidence.
2. Managing Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare is a highly regulated field, so CRM software for healthcare has to abide by the different national and international laws. Patient data protection may involve some unique policies in distinct regions, which complicates compliance. The developers need to know what changes in the regulation system have occurred and adapt safety control checks to be included in the developmental process. Failure to adhere to the rules attracts lawsuits and legal losses for healthcare organizations.
3. Handling Data Integration
As with most software, CRM software for healthcare must be integrated with other accumulated systems, such as EHRs, billing services, and scheduling calendars. However, this process can be cumbersome because of the format of data, old structures, and technological incompatibilities. Application developers must create APIs and connectors that will facilitate the interconnection of systems and provide accurate integrations.
4. Designing for a Diverse User Base
CRM software for healthcare is used by various members which include physicians, nurses, managers, and customers. Every group is different from the other regarding its requirements and the specific demands it will make to a consultant. For example, doctors may need easy and fast access to patient records. The patients, on the other hand, may only need easy ways to schedule their appointments. Sophisticated applications are used today to support various users presenting different needs. Designing an interface to support all these users can be challenging because it concerns effectiveness and simplicity.
5. Managing High Data Volumes
Auto-, para-, and micro-clinical data are typical big data in healthcare organizations: records, appointments, and treatments. CRM software for healthcare cannot afford to allow the management of this type of data to affect its efficiency. It will be the responsibility of developers to make it easy to scale the system. It should be able to handle large volumes of data, and proper database design has to be done.
6. Providing Real-Time Accessibility
The major types observed in healthcare include real-time accessibility of information. CRM software for healthcare should be able to afford users quick and accurate data access regardless of location. This can be very hard, especially when data connections are very scarce. Current and prospective developers should consider enhancing the design and functionality of their systems, relying more on devices and networks.
7. Balancing Costs and Customization
Automating patient and customer relations within an organization can be made easier through CRM software for healthcare. The provided software is tailored to suit the strategic needs of an organization. The development costs and time can be slightly high. The primary problem is corresponding, highly localized features while adhering to a specific budget line. A large amount of functionalities are necessary to implement. Developers need to understand which of them has the highest priority. Thus, they should be implemented first, while the resources are limited.
8. Testing and Maintenance
This is important not to release software that does not meet the expected performance by users of CRM software for healthcare. Testing in a healthcare environment needs caution and rigorous date adherence to healthcare timelines. Also, the post-go-live support of the software helps in fixing new problems, delivering updates, and ensuring compliance with new regulations.
When these issues are identified and dealt with, it is possible to design robust, effective Healthcare CRM software systems to respond to the needs of the healthcare sector. Challenges faced when implementing such processes include technical issues, planning issues, and issues involving healthcare processes. Thus, it calls for the integration of all three in the process. An effective system in the long run benefits patients, makes processes more efficient, and efficiently organizes users’ trust in the system.
V. Best tech stack to use when developing CRM software for healthcare
Selecting the best technology, tool, or platform to build trusted and high-performing CRM software for healthcare. A good tech stack needs to be chosen in such a manner that it runs smoothly, is scalable, and is secure. They are required for healthcare apps. Here’s a detailed guide to the essential components of a tech stack when developing CRM software for healthcare:
1. Backend Technologies
This area, known as the backend, deals with data and server-side tasks of the system’s working. For CRM software for healthcare, popular choices include:
- Node.js: It is well-known for its velocities and request handling. And it is perfect for real-time services.
- Python: Due to its ease of use and availability of large frameworks, namely Django or Flask. It serves well in developing secure and scalable systems.
- Ruby on Rails: It provides fast development with integrated tools, which will be perfect for startups and projects within a short period.
2. Frontend Frameworks
The front end is the part of the application that users deal with. That makes it necessary for it to be as easy to use as possible and as fast as possible. Effective CRM software for healthcare often uses:
- React: Offers the organization a rich and interactive interface that can be easily navigated by the user.
- Angular: Provides a good number of tools for building rich and engaging applications.
- Vue.js: It is a fast, light application that can build up user-oriented designs.
3. Database Management
- Healthcare organizations deal with huge amounts of information that are often sensitive. So, a dependable database is called for. Common options include:
- MySQL: An open-source DBMS that finds wide usage and is known for its high performance and stable operation.
- PostgreSQL: They are used for solving some difficult inquiries and for checking the accuracy of the information.
- MongoDB: A NoSQL database well designed for unstructured or semi-structured data.
4. Cloud Services
Healthcare CRM software, therefore, requires cloud services for scalability and efficient access to the data that they deal with. Popular cloud platforms include:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Aims to provide all kinds of services, starting from storage to computing powers and machine learning tools.
- Google Cloud: Includes powerful analysis tools and allows for linking with other applications of the Google package.
- Microsoft Azure: Popular due to its security and integration with corporate environments.
5. Security Tools
Security is quite important for CRM software for healthcare as it deals with sensitive information relating to patients. Incorporate tools and protocols such as:
- OAuth and OpenID: For user’s safe authentication.
- SSL/TLS encryption: It is for data protection in transmission.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: For protection against cyber threats, they have also been used
6. API Development
APIs are essential to connect healthcare CRM software to other systems, such as EHR, billing platforms, and patient portals. Swagger and Postman are the tools that aid in designing and testing APIs at the same time. REST and GraphQL are API standards well-recognized among Web service developers.
7. Analytics and Reporting Tools
Clients use the data, and people in the healthcare industry depend on the information to make effective decisions. This way, while incorporating analytics tools, the software includes real-time reporting and data visualization capabilities. Additional features associated with data analysis, and data reporting can be improved by using frameworks like Tableau or Power BI.
8. DevOps and Deployment Tools
Tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and Jenkins make these flowcharts efficient and flowing for continuous development and deployment. These tools are critical in constructing healthcare CRM software that is easily scalable to meet the user’s needs.
Thus, developers can ensure healthcare CRM software is protected, extensible, and easy to operate if they choose the proper tech stack. Integrating sound and highly developed backbone technologies with simple-to-use and well-developed frontend architectures and setting security precautions are necessary. They will result in producing a system that answers the needs of healthcare givers and patients. Choosing the right tools at each stage of development will enhance the process of delivering efficient software to improve healthcare results and organizational procedures.
VI. Building custom Healthcare CRM Software with Adamo Software

CRM software for healthcare developed and distributed by Adamo Software is designed to meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations. First, we identify client needs. Second, we create easy-to-use interfaces. And then we decide upon the technologies to be implemented. We progress basic functionalities comprising patient handling components and communication platforms. And we have powerful analytical tools that are HIPPAA and GDPR compliant. Segregation of strong security measures ensures the patient’s data stays personal and safe from different unauthorized parties.
Adamo Software also carries out Medical Healthcare CRM software testing to determine its efficiency. We handle various aspects of successful implementation, including the ability to map the CRM with other systems such as EHR and billing systems. After delivery, we avail ourselves of minor corrections and additions and help for efficient running of software products. With our knowledge, Adamo Software presents customized and highly beneficial services for the healthcare software industry. We will help to enhance patients’ outcomes and organize the work effectively.





