What is Health Data Management? Benefits, Challenges and HDM Software
Health data management is becoming more and more crucial in this digital world. Explore its benefits, challenges and HDM software for better patient experience.
In recent years, healthcare industry has seen significant advancements with the introduction of electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), and health information exchanges (HIEs).
In the US, nearly 4 in 5 office-based physicians (78%) and almost all non-federal acute care hospitals (96%) have adopted certified EHRs. Providers must continue to be transparent and give patients autonomy, making access to their own health data important.
With virtual care becoming more prevalent, health data management – the collection and sharing of data – is now more critical than ever. Patients can assist providers with data collection by sharing their data from home. Patient-centered care puts the patient in the front seat, working alongside providers.
With the right health data management software in place, healthcare organizations can better understand and manage their health data, leading to improved outcomes and better decision-making.
Let’s take a look at why it’s so important and how it all works.
I. What is Health Data Management
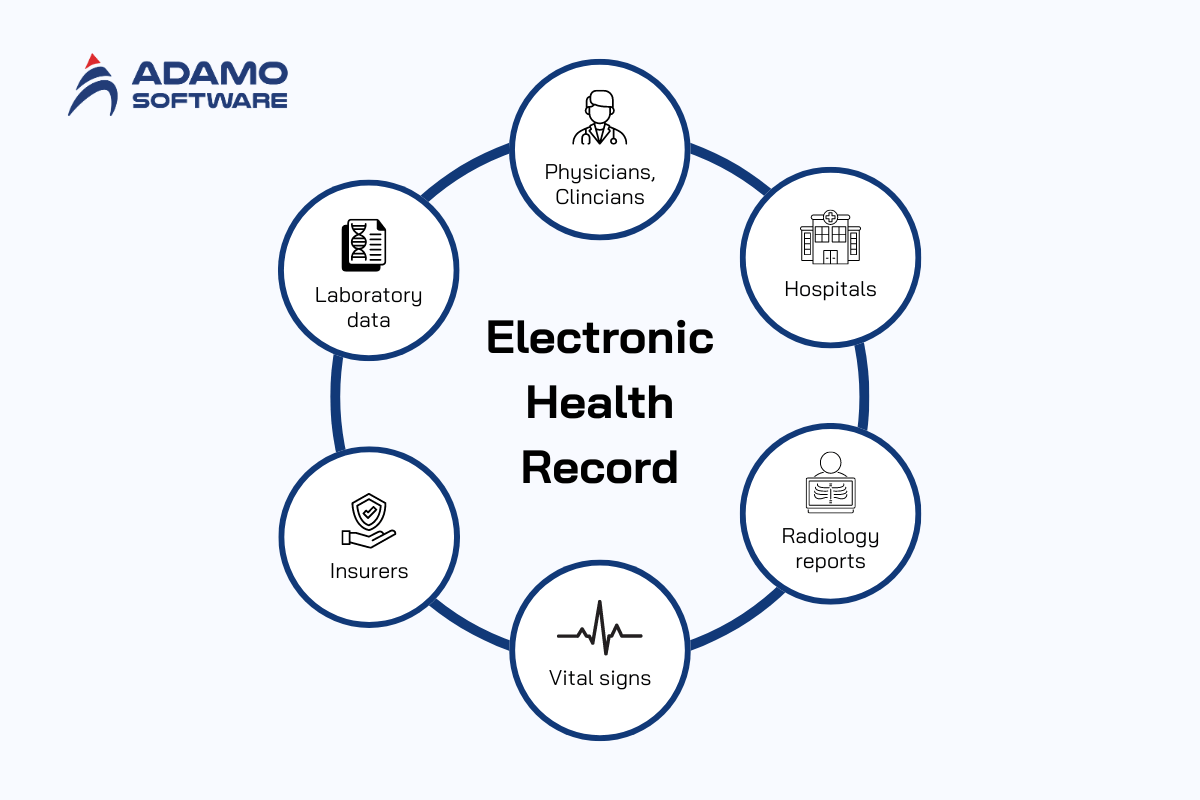
Health data management, also sometimes referred to as Digital Health data management, is the systematic organization of health data in digital form.
This can be anything from Electronic Medical Records (EMR) generated because of doctor visits, to Electronic Health Records (EHR), to handwritten medical notes scanned to a digital repository.
What’s more, health data includes but is not limited to:
_ Patient information
_ Medical notes
_ Laboratory test results
_ Procedures and surgeries
_ Prescriptions
_ Referrals and other communication
_ Provider information, etc.
Besides, Health data management (HDM) is the processing of managing the lifecycle of health data. Data is created, stored, organized, processed, archived, and destroyed. In addition, data is kept secured and protected to maintain a strict level of confidentiality and integrity and is only available to those who need access.
Healthcare database management systems have the capability to do all of this and more such as analyzing disparate and diverse datasets from multiple internal and external sources to deliver operational and decision support to applications, devices, and people.
Health data management, or Digital Health data management, is all about organizing health information in digital form. Health data can be collected from various sources like Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) from doctor visits, Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and scanned handwritten medical notes.
What’s more, health data can include:
_ Patient information
_ Medical notes
_ Lab test results
_ Procedures and surgeries
_ Prescriptions
_ Referrals and other communications
_ Provider information
Health data management involves managing the entire lifecycle of health data. This means creating, storing, organizing, processing, archiving, and eventually destroying the data. It’s also about keeping the data secure and private, so only authorized people can access it.
Healthcare database management systems can handle all these tasks. They also analyze various datasets from multiple sources to support operations and decision-making for applications, devices, and people.
II. Benefits of Data Management in Healthcare
To provide better care, healthcare providers need to stay informed about their patients and connect their health data with the latest evidence. But time is typically limited, and providers may not always have the resources to thoroughly review every patient’s records.
And, it’s important to improve both the quantity and quality of health data. The more accurate and comprehensive the data, the better decisions can be made, leading to better patient outcomes.
To achieve this, we need to include more relevant information in patient records, ensuring they are complete, up-to-date, and validated. More data allows for more thorough interpretation, though this can become complex as the amount of data grows and as new scientific guidelines and treatments emerge.
Here are some benefits of health data management that you can look for:

_ Better health data analytics: Healthcare data analysis software allows us to make predictions about patients’ health, enabling better treatment and a more proactive approach to healthcare, so that improve health outcomes for both individual patients and the general public.
_ Better alignment and communication: With digital records, communication between patients, providers, and other stakeholders improves. A comprehensive view of the patient facilitates better collaboration among doctors, even across different geographic locations.
_ Enhanced patient engagement: With health data records, patients can acknowledge their current health status, therefore understand their treatments, recognize trends, and take proactive care measures.
_ Data-driven decisions: Historical and real-time data also help improve decision-making for both providers and patients, reducing the reliance on guesswork and improving diagnostic accuracy.
_ Integration with personal health activities: Data from personal health activities, like those tracked by sensors or mobile apps, can be integrated into health records, then enhance treatment plans.
_ Clinical research and evidence-based medicine: High-quality, comprehensive datasets support clinical research by identifying potential participants, conducting studies, evaluating treatment outcomes, and developing evidence-based guidelines.
_ Compliance and privacy: Modern data management systems ensure compliance with privacy and security regulations, protecting patient information through encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
A well-organized health data management system supports various use cases, including chronic disease management, faster clinical trials, optimized provider resources, better wellness programs, and improved alignment between payers and providers.
III. Challenges of Health Data Management
Personal information is extremely sensitive, especially in the healthcare industry. Protecting patient data from potential breaches and cyber threats is crucial, requiring high-security standards set by local laws and jurisdictions. Internal restrictions within organizations ensure that only relevant staff members have access to this sensitive information.
Health organizations must ensure that data is shared securely to improve healthcare outcomes and shift to a value-based care delivery model, moving away from the current inefficient fee-for-service model. This also protects patient data from unauthorized access, such as ransomware attacks. Besides, data protection must comply with regulations like the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Health data management systems must adhere to government regulations for role-based access, encryption at rest and in transit, and be resilient against cyber-attacks.
What’s more, integrating health data from various stakeholders, including patients, providers, creditors, payers, and the government, is really important. Combining clinical, operational, and financial data with external population health data and other social determinants of health enhances public health data management.
As a healthcare provider, you must know that the quality of the data depends on what is fed into the database and how well it is organized. Fragmented data spread across several platforms can be challenging when these platforms need to communicate with each other. It’s important to use international standards for storing, labeling, classifying, transferring, and retrieving data.
Technology-related challenges also arise. The database must be scalable to handle the collected data and be able to consolidate data from various technical platforms and sources. That’s why healthcare provider data management and hospital data management systems must meet these requirements. Cloud enterprise data warehouses and data marts can be effective solutions to address these issues.
III. What is Health Data Management Software
As the healthcare industry evolves, health data management tools are becoming increasingly crucial for improving patient outcomes.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR) System
EHR system is the foundation of health data management. They provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, including diagnoses, medications, allergies, lab results, and more. By reducing medical errors, increasing efficiency, and enhancing communication between providers, EHR systems help improve patient outcomes.
2. Health Information Exchange (HIE) Networks
HIE networks enable healthcare organizations to securely share health data across different locations and organizations. Thanks to this comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, even if they’ve received care from multiple providers, it leads to better-coordinated care and improved patient outcomes.
3. Clinical Decision Support (CDS) System
CDS system uses health data to provide real-time information and evidence-based recommendations, helping healthcare providers make better clinical decisions. So that healthcare organizations can increase efficiency and enhance the quality of care.
4. Population Health Management (PHM) System
PHM system is another health data management software, which helps care providers manage the health of patient populations by identifying at-risk patients and providing targeted interventions. It reduces hospital readmissions, improve patient compliance, and lowers healthcare costs, all contributing to better patient outcomes.
5. Business Intelligence (BI) Tool
BI tool, on the other hand, allows healthcare providers to analyze and visualize health data in an easy-to-understand way. This Healthcare BI Software can identify trends and patterns from various data sources, so that providers can make informed decisions, leading to improved quality of care and better patient outcomes.
Also read: How to Implement Healthcare Data Warehouse: Benefits, Architect, Cost
IV. How Health Data Management System Helps Health Organizations
Data integration and management are vital in healthcare, ensuring medical care is provided efficiently and effectively by streamlining data and securing accurate record-keeping.
So, with such vast amounts of data, how do we ensure it’s transmitted safely and accurately?
1. Healthcare Data Governance
Establishing a single source for master data – known as the “source of truth” – is crucial. In this step, patient and provider identifiers and reference details like common vocabularies used in daily operations. Healthcare BI tools support these processes, leading to better outcomes.
2. Healthcare Data Integration
Effective data management involves integrating data from various sources in healthcare through EMR integration services. Adhering to federal regulations, such as HIPAA compliance, ensures interoperability between departments and systems like EHRs, labs, and insurance claims. This secure integration allows for seamless patient record access.
3. Healthcare Data Enrichment
Data enrichment uses AI and machine learning to identify meaningful patterns and insights in raw data. Natural language processing converts this data into discrete information for quality measurement or customized analytics. Anonymizing customer info also can create valuable marketplace platforms, providing extra value to vendors.
4. Data Storage in Healthcare
The final step in the data processing journey is integration and storage. This ensures a secure repository of information for drawing insights. By combining structured, unstructured, and semi-structured content into a standardized format, analysis can run smoothly across any platform or system.
5. Steps to Ensure Safe and Accurate Data Transmission
_ Establish clear governance: Implement a master data management system that maintains accurate and consistent data.
_ Ensure compliance: Comply with federal regulations like HIPAA to guarantee data interoperability and security.
_ Integrate efficiently: Use EMR integration services to gather and unify data from multiple sources.
_ Leverage AI and ML: Enrich data to gain valuable insights and improve decision-making.
_ Secure storage: Store data in a standardized, secure format to facilitate easy access and analysis.
VI. Why Adamo Can Help You Build a Bespoke Health Data Management System
At Adamo, we understand that effective health data management enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and provide timely interventions.
We are confident in providing end-to-end healthcare software development services, from fully-functional prototypes to design, MVP development, and deployment.
Our health data management system development solutions adhere to key healthcare software security standards, regulations, and best practices in real-time. We ensure the security of your healthcare solutions, ensuring sensitive patient and medical information is protected. Adamo understands health information privacy standards (GDPR, HIPAA) and complies with ISO 9001:2015 certifications.

VII. FAQs about Health Data Management
1. What database is commonly used in healthcare?
The prevalent choice is the HL7 Standard-Compliant Database (SCDB). It offers standardized structures for clinical and administrative data storage, ensuring interoperability with various software systems like EHRs and analytics tools.
2. How does data governance impact health data management?
Data governance establishes policies and procedures for managing data effectively, ensuring data quality, privacy, and security. It creates a structured framework that helps healthcare organizations maintain accurate, reliable, and compliant data.
3. What is data integration’s role in health data management?
Data integration merges data from different sources to provide a unified view, facilitating comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making. So that healthcare providers can gain a holistic view of patient health, improve coordination of care, and enhance overall healthcare delivery.
4. How do healthcare organizations comply with data privacy regulations like HIPAA?
Organizations comply with regulations like HIPAA by implementing strict privacy policies, securing data transmission and storage, and ensuring only authorized access to patient information.





