Understand Healthcare Compliance Management in Healthcare Entity

Healthcare compliance management involves a variety of local, state, and federal regulations designed to prevent fraud, waste, and abuse in the healthcare industry.
Ignoring these rules can lead to serious issues like fines, cyber risks, and damage to reputation. Healthcare compliance covers the confidentiality and handling of patient information, ensures the quality of patient care, prevents fraudulent activities, and protects healthcare workers.
Let’s take a detailed look at important healthcare laws, acts, and regulations, and how technology can assist in managing healthcare compliance. Compliance professionals must continually observe and update these standards to maintain adherence.
I. What is Healthcare Compliance
Healthcare compliance management means following rules, laws, and standards that apply to healthcare organizations and workers. It covers many areas, like keeping patient information private and meeting safety standards. Compliance programs help stop fraud, protect patient data, and make sure healthcare services are high-quality.
A strong compliance culture encourages everyone in the healthcare organization to prevent, find, and fix problems that could lead to fraud, waste, or abuse. This culture is built on a structured plan with specific steps, known as compliance elements. Besides, terms like ethics, culture, and code of conduct are often mentioned in documents about compliance.
You can explore more about Outsourcing Healthcare Software Development: Here’s when it works here.
II. Core Elements of Healthcare Compliance Management
The US Sentencing Guidelines for Organizations outline seven essential elements for an effective compliance program. Here’s how these elements are addressed in healthcare compliance management:
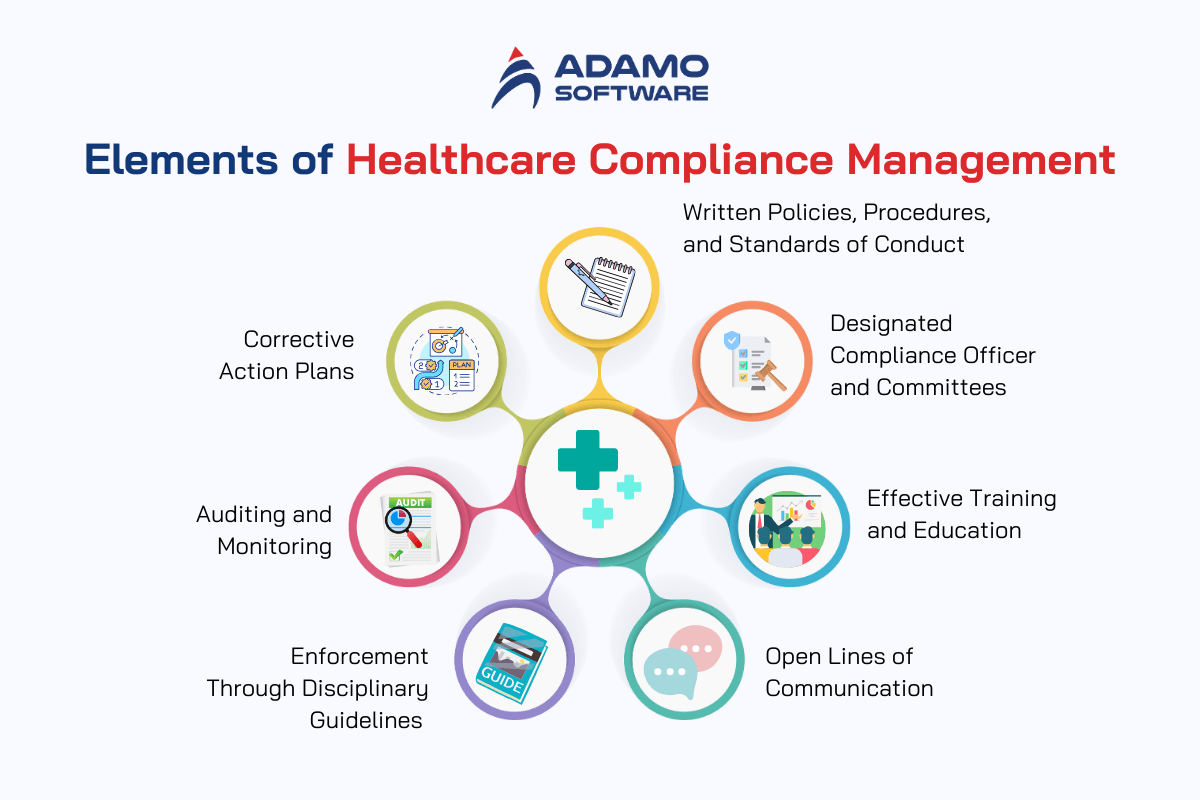
1. Written Policies, Procedures, and Standards of Conduct
_ Create a comprehensive plan covering all aspects of compliance
_ Define the ethical standards for the organization
_ Ensure everyone understands and follows the compliance guidelines
_ Prepare for unexpected events
Policies should apply to all employees, volunteers, and management. They should be created proactively and updated regularly to stay current with laws and organizational values.
2. Designated Compliance Officer and Committees
_ Appoint a compliance officer and establish committees
_ Define roles and responsibilities, meeting schedules, and communication methods to ensure the compliance program’s success
3. Effective Training and Education
_ Ensure staff understands the compliance program through access, education, and enforcement.
_ Provide training for new employees and regular refresher courses.
_ Develop a management system to handle documents, distribute policies, and track compliance.
4. Open Lines of Communication
_ Promote a culture of openness where staff can discuss compliance issues without fear.
_ Clearly outline communication methods and contacts for compliance-related questions.
5. Enforcement Through Disciplinary Guidelines
_ Develop a plan to enforce compliance, including policy distribution, training, and disciplinary actions for non-compliance.
_ Use a policy management system to notify employees of new policies and ensure acknowledgment.
6. Auditing and Monitoring
_ Regularly audit the healthcare compliance management program to ensure its effectiveness.
_ Create follow-up plans for addressing issues found during audits.
_ Use automated systems to manage policy updates and access for the compliance team.
7. Corrective Action Plans
_ Include steps to address and correct compliance violations.
_ Detail how to identify, confirm, and handle violations, including notifying relevant parties and taking disciplinary action.
_ Adjust the compliance program to prevent future issues.
These core elements help you create a robust compliance program, emphasizing education, communication, and proactive measures to foster an ethical culture. Although they derived from a Medicare manual, they’re beneficial for any healthcare organizations. Similar guidelines can be found on the OIG site.
III. Common Healthcare Compliance Regulations
Protecting patient data is vital in healthcare, and various regulations have been implemented to ensure its security. Here’s 8 significant healthcare regulations you must care about:
1. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) (1996)
HIPAA is the most well-known data privacy law in the U.S. It established the HIPAA Privacy Rule, which sets national standards for protecting health information, and the HIPAA Security Rule, which sets security standards for electronic health information.
2. HITECH Act (2009)
The HITECH Act enhances HIPAA by increasing penalties for data breaches and promoting the use of electronic health records (EHRs). It underscores the importance of secure electronic health information exchange.
3. 21st Century Cures Act (2016)
This act promotes scientific innovation, reduces administrative burdens, enhances data sharing, strengthens privacy protections, and improves overall patient care.
4. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) (2018) (EU)
While not a U.S. regulation, GDPR affects U.S. healthcare entities dealing with European patients. It enforces strict data protection rules, including health data, and requires informed consent for data processing, with significant fines for non-compliance.
5. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) (2020) (California)
CCPA gives California residents rights over their personal information, including health data. It requires businesses to disclose data practices and allows individuals to request data deletion, enhancing patient data protection.
6. HITRUST CSF (Health Information Trust Alliance Common Security Framework) (Various)
HITRUST is a framework, not a regulation, that helps healthcare organizations align with multiple security and privacy standards as it offers a comprehensive approach to safeguarding patient data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
7. Information Blocking Rule (2021)
Enforced by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC), this rule prohibits practices that hinder patient data sharing, and it also promotes interoperability while ensuring patient data security.
8. Interoperability and Patient Access Final Rule (2021)
Enforced by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), this rule requires healthcare providers to share electronic patient data upon request, giving patients more control over their health information and enhancing data protection.
IV. How to Ensure Healthcare Compliance Management
As a healthcare leader, it’s important to follow laws and set up compliance measures to avoid big penalties. Here’s a simple guide to help you ensure healthcare compliance management:
Step 1. Stay Informed
First, learn about the regulations that apply to your organization. As Regulations change often, keep yourself updated. You can do this by checking updates from government agencies, attending industry meetings, and reading relevant news. If understanding these regulations is hard, consider hiring a legal expert to help. You can also form a team within your organization to keep track of these changes.
Step 2. Implement Policies and Procedures
Once you know the regulations, create clear and simple policies and procedures that follow these rules. Then, make sure your employees understand them. Explain why these policies are important and involve your employees in creating them to increase their commitment. You also need to set up penalties for breaking these rules to ensure everyone follows them.
Step 3. Conduct Internal Compliance Audits
Remember to regularly check if your organization is following the rules. Start by identifying risky areas and prioritize them based on their impact. Next, develop a plan for audits and schedule them regularly. During audits, you should look for any issues and fix them. Use the findings to improve your policies and procedures.
Step 4. Adopt Compliance Tools
Using technology can make compliance easier. Compliance tools can help you monitor and follow regulations.
Here are some recommended tools:
_ Visitor management system: Make sure compliance with regulations like social distancing and health declarations, and tracks visitor footfall.
_ Billing compliance software: Keep sensitive information secure, flags billing or coding errors, and ensures compliance with privacy acts.
_ Vaccination management system: Automate the verification of workers’ vaccination statuses and adjusts entry policies based on state regulations.
V. Best Practices for Healthcare Compliance Management
Healthcare compliance management today focuses on program improvement and efficiency. Alongside the core elements defined by OIG, here are some best practices you can consider:

1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
To manage the complex healthcare landscape, organizations must conduct regular risk assessments like identifying potential compliance risks and implementing strategies to mitigate them so that you can stay ahead of evolving regulations and industry trends.
2. Create Metrics for Program Evaluation
Creating measurable metrics is important for tracking the effectiveness of healthcare compliance management programs. Metrics can include the percentage reduction in compliance violations, improved employee training completion rates, and enhanced patient data protection measures. These indicators allow you to gauge the impact of their compliance efforts and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
3. Learn from Successful Practices
Learning from other organizations’ successes allows healthcare providers to adopt proven strategies tailored to their specific needs and challenges. Adapting best practices from others can encourage innovation and efficiency, but it’s important to customize these practices to fit your organization’s values, mission, and healthcare environment.
4. Implement and Monitor Best Practices
Putting best practices into action is key to strengthening compliance programs. Continuous monitoring of these programs helps organizations remain agile, adjust strategies as needed, and show a commitment to both compliance and ongoing improvement.
5. Encourage Whistleblowing
Whistleblowers are vital in maintaining the integrity of the healthcare industry by exposing misconduct, fraud, patient endangerment, and regulatory violations. Creating an environment where whistleblowers are protected and encouraged to come forward is crucial for transparency and accountability.
6. Use the Three-Line Model
Collaboration between compliance officers and operational leaders can be challenging due to a lack of awareness about shared responsibilities. The Three Lines Model, developed by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), can address this by defining three lines of responsibility:
_ First line (operational areas): Identifies and mitigates risks within their departments, working with compliance for monitoring.
_ Second line (compliance, general counsel, risk, and quality): Provides training, creates policies, audits, and monitors for operational leaders.
_ Third line (independent oversight): Involves internal auditors or independent consultants to assess compliance with policies, procedures, laws, and regulations.
This model emphasizes that healthcare compliance management is a shared responsibility across the organization.
Combining the three lines model with best practices like the OIG’s seven elements for compliance program effectiveness and establishing operational compliance committees, you can foster a collaborative approach that highlights the importance of shared responsibilities in healthcare compliance management.
V. How can Technology Help you with Healthcare Compliance Management
Regulatory compliance is one of the most expensive aspects of running a hospital or clinic. Hospitals and providers must adhere to these regulations, no matter the cost, and rural health facilities often feel these pressures even more.
Many rural hospitals and clinics already face significant challenges, including high disease levels, geographical barriers, and an aging patient population. And the ongoing shortage of skilled workers exacerbates these issues.
But hospitals can mitigate staffing shortages, inflation, and regulatory pressures through the strategic use of technology. Smart deployment of technology allows hospitals to focus their resources on the most critical initiatives.
Rural providers face unique challenges, such as limited IT budgets and staff, making technology implementations difficult. These hospitals are already stretched thin, and staff prefer to concentrate on patient care rather than regulatory compliance tasks.
To be effective, technology needs to be user-friendly and customizable to meet the specific needs of the practice. It’s not just about having technology but using it efficiently to address long-standing issues.
Technology can simplify the complex regulatory environment, from training initiatives to managing electronic health records (EHRs) and protecting patient data. It can streamline the management of insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid regulations, reducing the administrative burden.
When used correctly, technology acts as a force multiplier, allowing you to reduce costs across an organization by minimizing errors, automating billing, and keeping patient records organized, freeing up staff to focus on patient care.
Technology also allows healthcare providers to identify and address health problems before they become more serious, especially for at-risk patients. Telehealth and wearable devices can enable doctors and nurses to see more patients and collect data remotely, reducing wait times and unnecessary office visits.
If you are on tight budgets and staffing shortages, you must adopt new approaches to long-standing problems to avoid repeating the same issues. While regulations cannot be eliminated, healthcare organizations can better position themselves to manage them.
VI. Adamo’s Healthcare Software Development Helps You Implement Healthcare Compliance Effectively
At Adamo, we provide healthcare software development solutions that adhere to key healthcare security standards and regulations. We ensure the security of your healthcare solutions and protect sensitive patients and medical information. Our services comply with GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 9001:2015 certifications.

We offer a range of healthcare development solutions such as TeleHealth / Telemedicine Solution, Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), On-demand Healthcare Solution, Wearable Medical Devices, allowing to implement technology for better healthcare compliance management. Our experienced IT developers understand healthcare regulatory requirements and are skilled at creating innovative healthcare software solutions.
If you need an IT vendor for better healthcare compliance management, Adamo is here to help.





