Decentralized apps: Definition, uses, and differences with normal apps

Decentralized apps, or DApps, are reinventing software and digital services as we know it. Decentralized apps differ from traditional apps, which are stored and controlled via centralized servers by a single organization. That means that they transmit data spread out among many nodes. As a result, they will have enhanced security, increased transparency, and resistance to censorship.
Anyways, why are so many more people paying attention to decentralized apps? Isn’t it quite obvious, especially in a world where we constantly talk about data privacy and control like this? Decentralized apps promise a user-centered approach where individuals have more ownership of their digital experiences.
In this article, we’ll look at the details of decentralized apps, practical use cases, and critical differences compared to traditional apps. If you’re new to dApps or just curious about future tech, this guide will explain exactly what makes decentralized apps exceptional.
I. What are Decentralized Apps?
Decentralized apps (DApps) are software programs that run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer (P2P) network and not a single central server. Unlike traditional apps, dApps are spread across a network and run by people who collectively use them. Often, most are deployed on platforms like Ethereum for various purposes. They can be for digital wallets, gaming, social media, exchanges, or personal finance.
Let’s take a different example, like Uber or X (formerly Twitter), to understand the difference. No matter how many users are involved, these apps run on a system operated by the company that owns and controls the backend. Hence, the app’s functions and data are within the company’s influence.
In contrast, decentralized apps work in different ways. They are on a P2P network or blockchain. Therefore, they are decentralized. What could this mean? For example, P2P programs such as BitTorrent, Tor, or Popcorn Time let users share and access content across an intranet of connected computers.
Moreover, decentralized apps run in a public, open-source environment on a blockchain, making them both open-source and public. It’s a decentralized system, so they are not under single authority control. For instance, a developer could create an X-like dApp on top of a blockchain where users can publish messages. Only the message’s creator can delete it when it’s posted, giving users more control over who could see it (and who might not).
II. How do DApps operate?
To learn about the operation of decentralized apps, there’s a term that we need to know: smart contract. Smart contracts define self-executing code describing rules that execute tasks on a distributed, peer-to-peer network. These are the foundations on which decentralized apps operate.
When the smart contract gets triggered after specific conditions are met, all nodes on the network perform the given task. As mentioned above, decentralized apps differ from traditional apps because they don’t rely on a central server. The nodes collaborate among themselves and run on top of consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work.
All the data, transaction records, and activity logs of dApps are stored in the blockchain and are transparent and secured by cryptography. The information is tamper-resistant and available to all the network participants thanks to the decentralized storage.
While dApps still provide user interfaces and experiences similar to web and mobile apps, its backend runs decentralized. This means it distributes authority and management to the network rather than having it controlled by a single point. With this setup, decentralized apps can continue to work even if the original development team has stopped.
III. What are the differences between DApps and normal (centralized) apps?
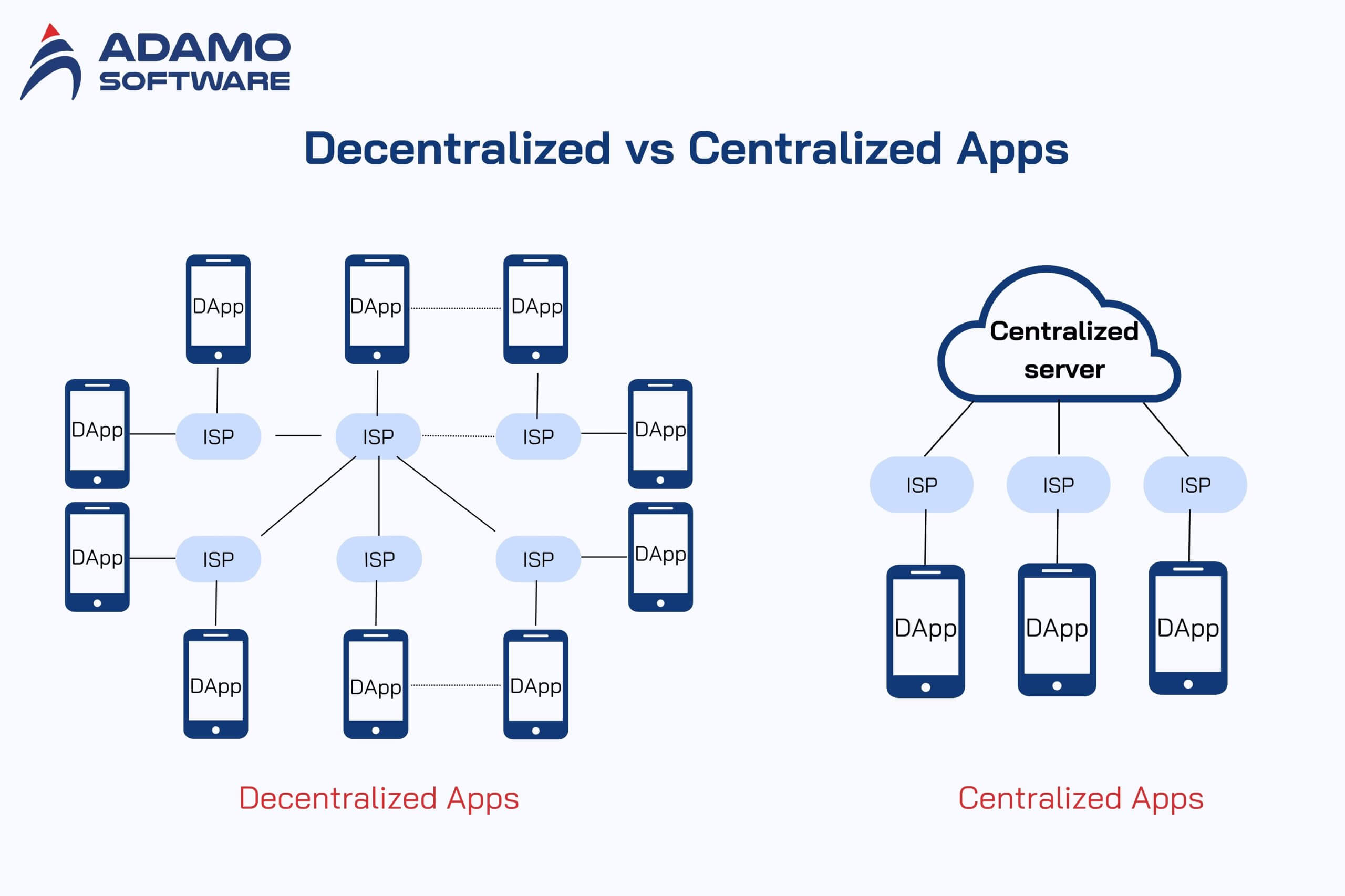
Before getting into the pros and cons of decentralized apps and how we can use them, let’s discuss further their differences from centralized apps.
Centralized apps are operated and owned by just one entity, with the application software running on servers managed by that same owner. With centralized apps, users can download a copy of the app and communicate with a company’s server to send and receive data. Overall, in this model, a central authority manages and maintains the system’s data, and users trust the owner to treat their data securely.
Decentralized apps, in contrast, run on a blockchain and/or peer-to-peer network of computers, where users can interact without central authority. Some dApps may be free, while others require the user to pay a cryptocurrency developer to access or use the source code.
Moreover, many dApps also rely on smart contracts. These are programmed to run automatically between the parties involved, eliminating the need for a trusted intermediary. This dependence on blockchain protocols gives more security to the network as information about the person is protected across the network.
IV. Pros and cons of decentralized apps
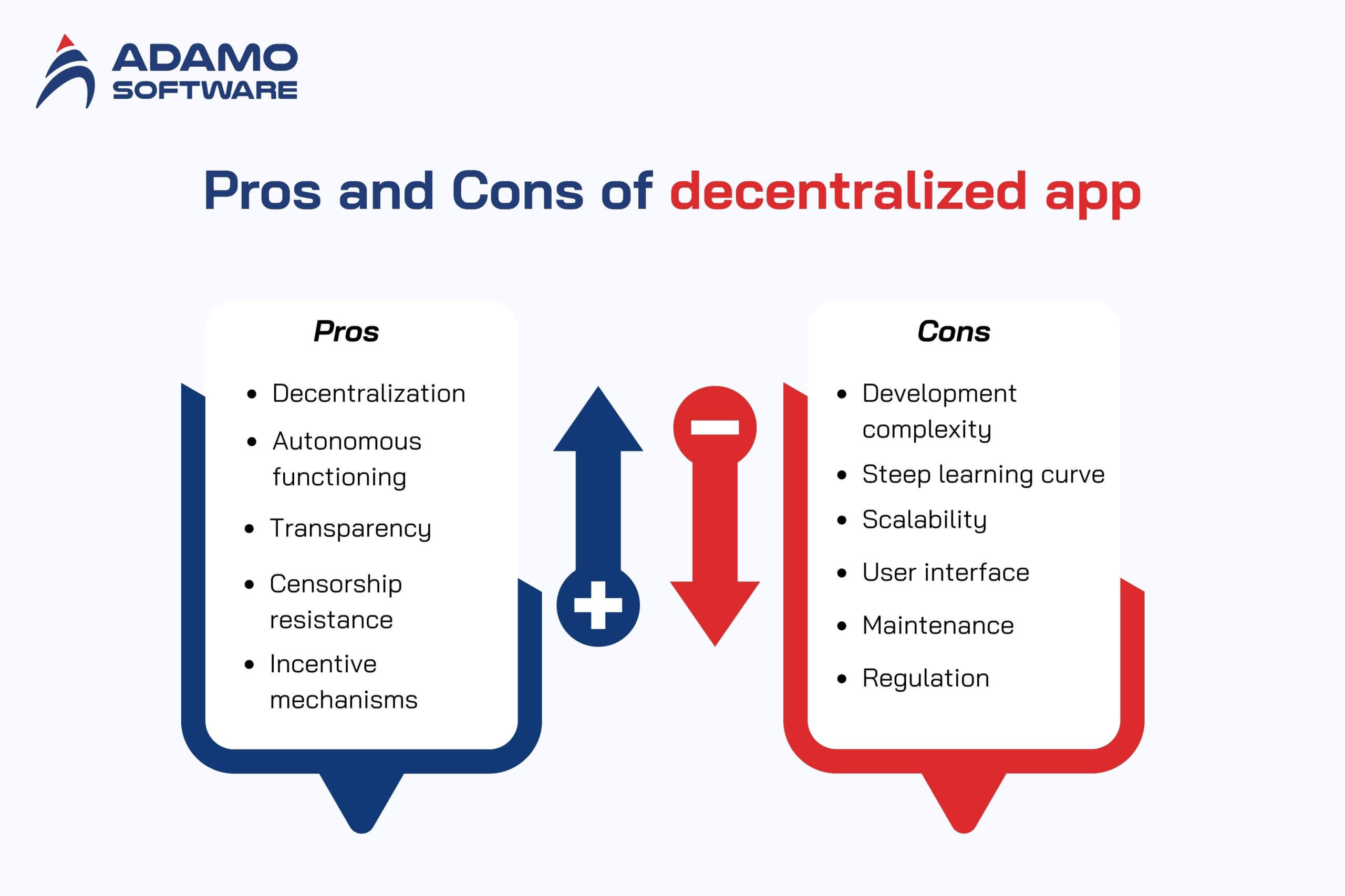
1. Advantages of decentralized apps
- Decentralization: Decentralized apps don’t have a central authority managing the platform. Its decentralization makes it much harder for governments and other authorities to shut down or censor dApps.
- Autonomous functioning: Smart contracts, pieces of code that automatically run once certain conditions are met, are how dApps work. This undoes the requirement of administrators, intermediaries, or anyone within the system’s tenure to manage and enforce operations.
- Transparency: The code for dApps often runs on open-source platforms, meaning anyone can and should review the code behind them. At the same time, transactions are being recorded onto a public blockchain, and any user can see the activity, building higher trust among users.
- Security: Since blockchain is a distributed technology, it is hard for hackers to compromise dApps. Data is distributed across the network, so altering information is nearly impossible without the consent of most current participants.
- Censorship resistance: dApps are much more complex to control or block than centralized apps. This results in users being able to access services and information freely regardless of regions’ regulations.
- Community-driven: Many dApps are developed, run, and controlled by a community rather than a centralized entity. It creates a culture of open collaboration and innovation, promoting user participation in the evolution and improvement of the platform.
- Incentive mechanisms: Incentives based on tokens are a significant part of many dApps, whereby users are drawn into the network in exchange for tokens. They allow users to trade, sell, and use these tokens often within the ecosystem. This then creates a financial incentive for them to use the platform.
2. Disadvantages of decentralized apps
- Development complexity: Developing decentralized apps is challenging, requiring developers to know about blockchain technology, smart contracts, and consensus mechanisms. It can slow down development and take up more resources.
- Steep learning curve: It isn’t easy for users to understand how dApps work and navigate their respective interfaces. This may complicate the user experience, given that the user is disconnected from its central administrators due to the blockchain concepts and decentralized nature.
- Scalability: During periods of high network activity, dApps struggle to process a large number of transactions. When demand for using blockchain gets high, blockchain networks have limited throughput, so transaction times become slow, and fees increase.
- User interface: Traditional applications have gone too far, and dApp interfaces often lack their polish and ease of use. Though they’re great for decentralization and technical stuff, oftentimes, they make things less user-friendly for the general user.
- Regulation: The legal field of dApps is still developing. Developers and users could be left confused as governments and regulators debate how to classify and regulate these platforms. It’s uncertain if the platform they built — or used — is compliant and whether some legal issues might arise later.
- Maintenance: It can be more challenging to update or fix a dApp because it is a decentralized dApp.
V. Popular uses cases of DApps
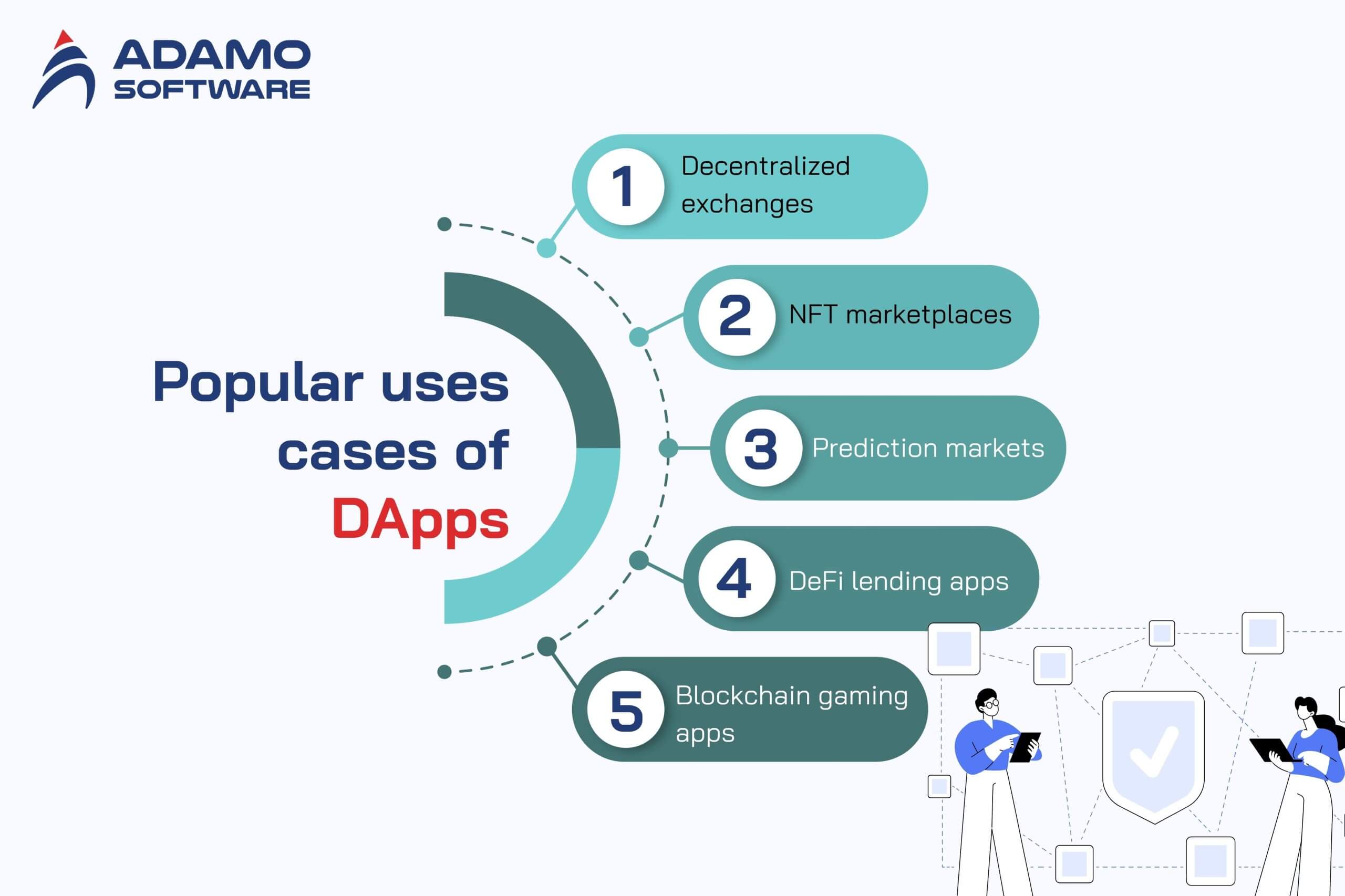
1. Decentralized exchanges
Uniswap and PancakeSwap are decentralized exchanges (DEXs), where users trade cryptocurrencies without centralized intermediaries. Originally, trading was done on centralized exchanges (CEXs). This is like a third party that connects buyers and sellers. However, it comes with some disadvantages. Therefore, the switch to decentralized exchanges is quite a bold but necessary step.
Decentralized exchanges address CEX’s security issues by offering more anonymity and non-custodial transactions. The actual assets traded never move through an intermediary with DEXs and, therefore, leaves the user with control over his or her funds. Hence, decentralized exchanges are many people’s claim for the future of cryptocurrency development.
As many benefits as they can bring, the application of decentralized apps for DEXs is still in its early stages. Specifically, they still have low trading volumes, which can be observed with some truly decentralized offerings like Radar Relay.
Additionally, decentralized exchanges may also find themselves in regulatory challenges. Authorities have voiced concerns regarding whether they should or should not be held to the same standards as their centralized counterparts.
2. NFT marketplaces
An NFT marketplace is a place for NFT creation, purchase, sale, and purchase. NFTs are unlike regular cryptocurrencies in that they’re not fungible or interchangeable in the same way as traditional currencies. Instead, they are unique digital tokens that can’t be swapped at a one-to-one ratio. This is what makes NFTs unique, and NFT marketplaces are emerging as the key hubs for trading NFTs.
NFT marketplaces use blockchain technology to authenticate and own each digital asset. When an artist or creator mints an NFT, they record it on the blockchain with a unique identifier. Therefore, it is guaranteed that every NFT is one of a kind. Once purchased, the ownership is added to the blockchain, and any transaction is transparent and within bounds.
Non-fungible tokens can be minted and traded in popular NFT marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible, bringing new digital economies. As a leader in the NFT space, OpenSea has one of the deepest and broadest marketplaces for NFTs. Here, you can find anything from art and music to domain names and virtual real estate. Its open protocol allows it to be quickly integrated with other platforms, and is a favorite of creators and collectors.
Rarible is different, as its community is empowered to vote for upgrades and changes on the platform. Rarible takes a unique ‘creator autonomy’ approach, giving independent artists a popular alternative. Specifically, it focuses on creator autonomy and providing the unique “RARI” governance token. These kinds of decentralized apps really allow creators to operate in a new digital economy free of old constraints.
3. Prediction markets
Decentralized prediction markets use the crowd’s wisdom to predict future events without compromising users’ identities. Like any futures contract, these markets enable speculators to bet on an event’s outcome instead of an asset’s price. Because anyone can open a trade, an opposing party is happy to bet on both sides in a decentralized prediction market.
Prediction markets have existed forever, creating a space where you bet on various events — political outcomes or economic trends, among other things. Nowadays, users engage in these markets using crypto assets, like stablecoins, for instance. Various protocols inside a crypto space allow you to build your prediction market, giving you flexibility and creativity.
These markets price the predictions according to what people will pay for their bets. Specifically, this is true of speculation for high-profile events (e.g., a presidential election), often priced higher than local sports outcomes. Participants can also bet on what will happen to the market if, for instance, a political candidate is elected.
Examples of decentralized prediction markets like Augur let users bet on many real-world events, such as economic growth or political elections. Centralized markets, on the other hand, are often plagued with conspired perceptions and limited by regulatory constraints. Decentralized markets, however, allow users to launch their own markets and control parameters. Hence, it makes liquidity and participation more open.
4. DeFi lending apps
Crypto lending is the act of lending cryptocurrency to someone in exchange for interest payments. While traditional lending often deals with banks, crypto lending can happen on centralized finance (CeFi) platforms or decentralized finance (DeFi) ones.
Another major difference is that with crypto loans, you don’t need a formal intermediary. Thanks to smart contracts, the lending process is automated. Everything from repayment schedules to interest rates is handled, making for less time and effort.
The focus here is on DeFi lending – which takes crypto lending to another level by eliminating intermediaries. Aave, MakerDAO, and Compound are platforms that lend and borrow cryptocurrencies directly using smart contracts. Generally, the transactions in these decentralized apps run automatically, keeping in control of their tokens with the users. DeFi lending protocols require borrowers to overcollateralize at least 110%, and interest rates are pegged to supply and demand.
Unlike CeFi lending, DeFi lending is permissionless, meaning that you don’t need to provide any KYC verification like CeFi lending. This means anyone can use DeFi lending apps as long as they have an internet connection.
In addition, DeFi protocols are trustless, meaning users can audit the code before committing funds. However, it’s essential to know that developers do not financially reimburse for coding bugs or security breach losses.
Overall, DeFi lending stands as a major shift in the direction of accessibility and transparency of the lending space. Platforms like Aave make lending and borrowing cryptocurrencies easy and secure, utilizing the advantages of smart contracts and decentralization.
5. Blockchain gaming apps
The blockchain gaming apps seamlessly combine NFT ownership of characters with the gameplay and money-earning mechanics, making the gaming experience truly innovative. It brought a fusion of cryptocurrency and video game design, ensuring players own these digital assets and interoperability across platforms.
Blockchain gaming transparently logs ownership of in-game items on an immutable public ledger, the same as a crypto transaction. Users own skins, weapons, and even smart virtual real estate, each of which has an actual monetary value.
These items can be tokenized as non-fungible Tokens (NFTs), with each item having a unique identifier that verifies its rarity and supply. Therefore, players can buy, sell, and trade them on various marketplaces.
Though blockchain gaming is not new per se, this paradigm shift by incorporating decentralized apps into the gaming ecosystem alone will empower players. Specifically, it gives them actual ownership of their in-game assets, and it also opens up new avenues for engaging the gaming community for monetization.
Also read: Build decentralized app: Brief guideline for starters (Cost included)
VI. Adamo Software turns your DApps ideas into reality
Adamo Software can be your trusted partner in turning your decentralized app ideas into reality. Based in Vietnam, we are highly skilled and capable of delivering high-quality and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.

With expertise in blockchain technology, we guide you through the entire development process, from concept to deployment, ensuring your DApp is innovative, secure, and user-friendly. Our commitment to a humanistic approach means we collaborate closely with you to ensure your vision is fully realized.
Having expertise in blockchain technology, we can support you throughout the entire development of decentralized apps, from the concept to the deployment. Adamo can ensure that your decentralized apps stay innovative, secure, and user-friendly.
As a company with a track record of successful projects, we pride ourselves on creating interactive products that really solve our customers’ problems.
Do you have this idea for a dApp that you want to turn into a market-ready solution? Contact Adamo Software today, and let’s begin this exciting adventure together!





