AI in Telemedicine: 6 Use Cases Transforming Virtual Care in 2026

Discover how AI is reshaping telemedicine – from virtual health assistants to predictive diagnostics. Explore 6 real-world use cases, tech stacks, and implementation challenges.
Patients are increasingly choosing telehealth because it lets them receive medical services and treatment from a distance, so they don’t have to go to a physical clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming healthcare by making telehealth more accessible, efficient, and focused on the patient. The current use of AI in telehealth is focused on enhancing patient care by boosting diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and improving patient monitoring. Let’s learn about the adoption of AI in telemedicine with Adamo Software!
Through this blog post, you will find out the following pieces of information.
- The importance of AI in telemedicine
- How does AI in telemedicine work?
- What are the benefits of AI in telehealth?
- Challenges and ethical issues in AI-powered Telemedicine
- Uses cases of AI in Telehealth
All information has been thoroughly researched and updated to the latest trends. So, let’s read our blog post and find some useful information!
I. The importance of AI in telemedicine
According to Medtech Intelligence, approximately 75% of healthcare organizations that have integrated AI have seen improvements in disease treatment, and 80% have reported a reduction in staff burnout. This number shows that adopting AI in telemedicine can be beneficial for both healthcare facilities and patients. Let Adamo Software discuss the importance of AI in telemedicine. Here are some reasons for using AI in telehealth.
- Early Health Risk Detection through Data Processing using AI algorithms
- Revolutionizing Healthcare with AI-Powered Diagnostics
- Innovations in Wellness with AI: providing a clear view of users’ physical health
- Empowering Patients with Accessible and Personalized Healthcare via AI
- Seamless Remote Monitoring for Continuous Patient Care with AI
Let’s delve into each reason to see the importance of integrating AI in telemedicine!
1. Early Health Risk Detection through Data Processing
Leveraging AI in telemedicine is helpful for detecting health risks early. Chronic diseases have become more common, with a notable increase among adolescents and young people. According to CDC, in the US alone, chronic illnesses like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes are a leading cause of death, accounting for nearly 75% of deaths worldwide each year. Many of these early deaths could be avoided with a greater focus on preventive care and lifestyle changes. AI tools can be seamlessly integrated into preventive care.
AI helps medical professionals more efficiently assess and interpret healthcare data. By rapidly processing large datasets, AI algorithms enable medical professionals to identify potential health risks at an earlier stage than using the traditional methods.
A prime example is the use of AI-driven diagnostic tools during the pandemic. These tools quickly analyzed chest X-rays and CT scans for signs of COVID-19 pneumonia, allowing for prompt medical intervention. Besides, adopting AI in telemedicine is especially valuable in oncology, where AI can enhance predictions of cancer risk by simulating disease progression.
2. Revolutionizing Healthcare with AI-Powered Diagnostics
Beyond analyzing data faster, AI in telemedicine has been making significant breakthroughs in the field of healthcare. This technology allows for the analysis of mammograms at 30 times faster speeds and with near-perfect accuracy, significantly reducing the need for biopsies.
Besides, AI in telemedicine also contributes to expanding the application of technology to reduce lung cancer mortality rates globally, a goal that AstraZeneca is actively pursuing. In addition, AI also supports the enhancement of CRISPR technology, a powerful tool in genome editing, allowing researchers to change DNA sequences and adjust gene function, opening up huge potential for future medicine.
3. Innovations in Wellness with AI
AI in telemedicine can also be applied in the wellness sector. AI tools have made major progress in the wellness industry, with wellness apps becoming a fast-growing part of the larger AI market. These apps are growing in popularity because of their advanced features, including personalized recommendations, real-time tracking, and predictive analysis. AI-powered apps provide personalized meal plans by assessing users’ dietary habits and nutritional needs. Thanks to this, users can meet their health goals with tailored dietary advice.
FitXpress is an outstanding example of using AI in telemedicine. This app uses body data to create personalized health insights and lifestyle tips, helping users achieve sustainable weight loss and better long-term health. Utilizing only two smartphone photographs, FitXpress provides users with a comprehensive 3D body model and more than 80 precise body measurements. It also calculates essential body composition metrics, including BMI, BMR, and body fat percentage.
With this data, users can gain a clearer understanding of their physical condition and monitor changes over time. Regular body scans allow individuals to track their progress, with the 3D models providing a compelling visual representation of their transformations, which can serve as a significant source of motivation. The platform’s AI-driven data helps businesses create customized exercise programs, optimizing fat loss and improving overall health.
4. Empowering Patients
AI in telemedicine plays an important role in helping patients access healthcare services quickly and conveniently. By analyzing personal medical data and medical history, AI can make appropriate treatment recommendations, remind people to take medicine or return for check-ups, and monitor health status in real time. This helps patients be more proactive in their health care and reduces the dependence on face-to-face visits. This is a particularly useful solution for people in remote areas or with limited mobility, when accessing medical facilities is difficult.
AI in telemedicine is a platform that empowers patients to take control and manage their own health. Through smart applications, patients can access their health records anytime, anywhere, monitor their body indicators, receive reliable medical information, and ask questions directly to doctors remotely.
Moreover, AI also helps patients make more informed decisions by providing data analysis and predicting health risks based on personal information. As a result, they can choose appropriate treatments, adjust their lifestyles in a timely manner, and prevent diseases more effectively.
5. Seamless Remote Monitoring
With the application of AI in telemedicine, patients are always monitored without having to visit the hospital regularly. Through smart wearable devices and medical sensors, data on heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygen levels or sleep quality are collected in real time and sent directly to the medical team. This allows for early detection of abnormalities and timely intervention, reducing the risk of complications.
AI technology not only records data but also analyzes patient health trends, predicts potential risks and automatically issues warnings. Doctors and medical staff can proactively adjust treatment plans, optimize medications and care measures based on actual conditions.
Generally, AI in telemedicine benefits both healthcare facilities and patients. Let’s keep reading to see how it works.
II. How does AI in telemedicine work?
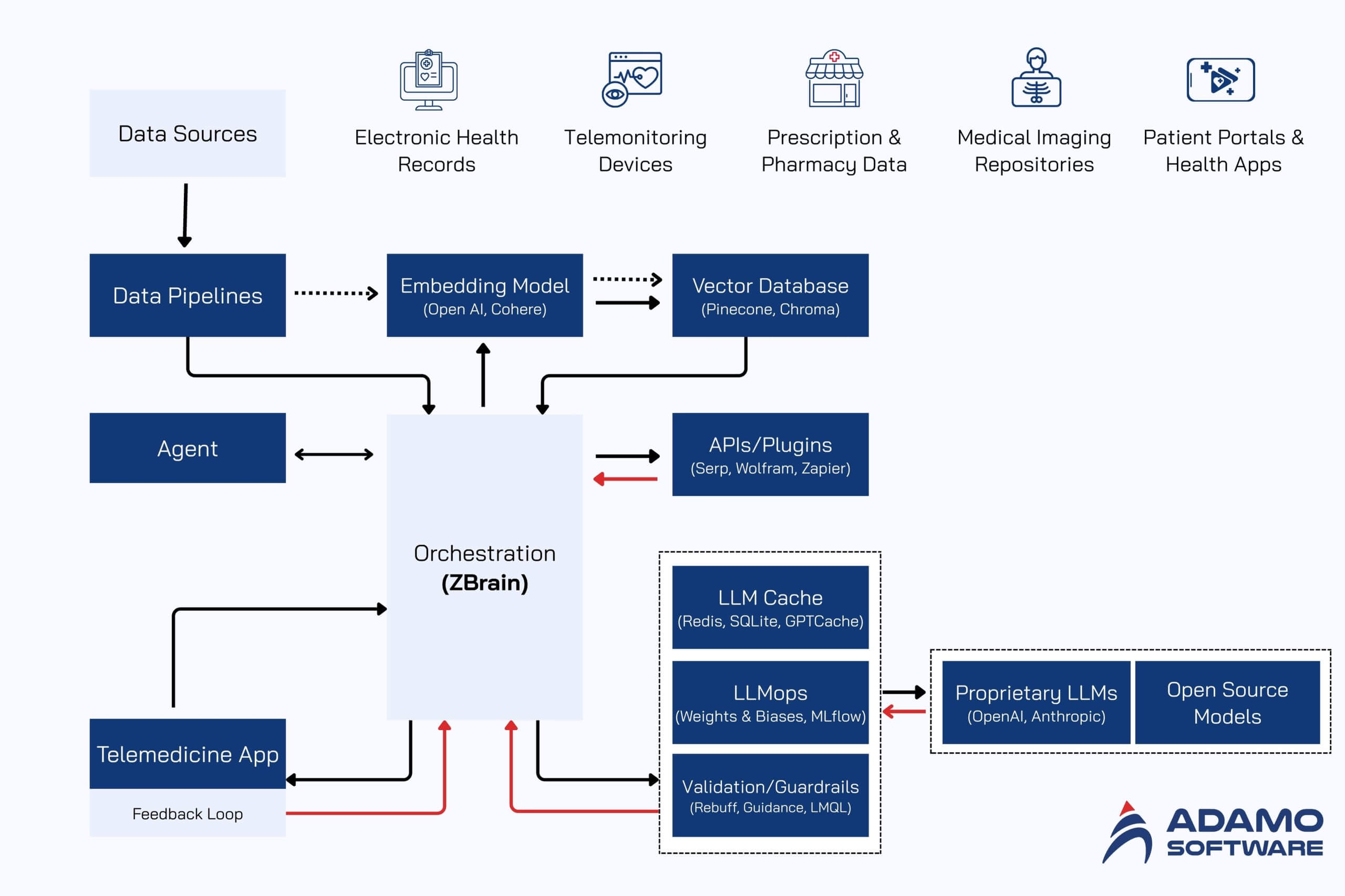
AI integration in telemedicine helps process large volumes of medical data, providing insights that support clinical decisions and patient care. This approach goes beyond traditional healthcare by using Large Language Models (LLMs) with an organization’s specific knowledge base.
This approach streamlines telemedicine, improves diagnostic accuracy, and helps professionals give more informed advice, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction. By combining several elements, this architecture optimizes telemedicine to ensure healthcare is delivered on time and accurately, overcoming geographical barriers. Below are 16 steps of the process.
- Data sources: gathering data from various sources
- Data pipelines: managing various tasks
- Embedding models: converting text into vectors for AI interpretation
- Vector database: streamlining querying and retrieval tasks
- APIs and plugins: linking components and adding functionality
- Orchestration layer: managing the workflow
- Query execution: covering medical practices
- LLM processing: query processing and orchestration
- Output: various forms
- Telemedicine app: core application
- Feedback loop: enhancing the LLM’s long-term accuracy and relevance
- Agent: solving problems and learning
- LLM cache: boosting the AI system’s speed
- Logging/LLMOps: logging actions and monitoring performance
- Validation: validating LLM’s outputs
- LLM APIs and hosting: handling telemedicine workflows and hosting the platform
Let’s see more detailed information about how AI in telemedicine works with Adamo Software!
1. Data sources
The process starts by collecting data from various telemedicine sources. Below are some types of data that you should collect when adopting AI in telemedicine.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital records of a patient’s medical history, including diagnoses, medications, and lab results.
- Telemonitoring devices: Real-time data from wearables like heart rate monitors, blood pressure cuffs, and pulse oximeters.
- Prescription and pharmacy data: Details on prescribed medications, dosage, and refill history for remote management and adherence.
- Medical imaging repositories: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans that healthcare providers can access for remote diagnosis.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These systems provide doctors with evidence-based guidelines and alerts during telemedicine calls to help them make informed decisions.
- Patient portals and health apps: Patients can use these to enter their own data, like symptoms and health metrics, which helps doctors monitor them and make more accurate remote assessments.
2. Data pipelines
Once you have finished collecting the data, you will process the information through data pipelines. They handle a range of tasks, including filtering, cleansing, and processing, preparing the data for analysis.
3. Embedding model
The processed data is broken into chunks and then sent to an embedding model. The model turns text into vectors, enabling AI to accurately interpret it. This task frequently utilizes established models developed by leading entities such as OpenAI, Google, and Cohere.
4. Vector database
The vectors are saved in a vector database, which simplifies querying and retrieval. These databases, such as Pinecone, Weaviate, and PGvector, are built to store, compare, and retrieve billions of these numerical representations.
5. APIs and plugins
When you integrate AI in telemedicine, you should not miss the APIs and plugins. APIs and plugins like Serp, Zapier, and Wolfram are essential for connecting components and enabling extra features, such as accessing data or performing tasks.
6. Orchestration layer
Orchestration layer is an essential aspect of AI in telemedicine, helping to manage the workflow. For example, ZBrain streamlines prompt chaining, handles external API interactions, and retrieves data from vector databases. By coordinating these tasks and maintaining memory across LLM calls, it generates the final prompts for the language model.
7. Query execution
When a user submits a query to the app, the process of data retrieval and generation begins. These queries of AI in telemedicine can cover medical topics, such as reviewing a patient’s history, analyzing a case, or planning a treatment.
8. LLM processing
Upon receiving a query, the application will send it to an orchestration layer, , which retrieves data from the vector database and LLM cache. It then forwards this information to an appropriate LLM, selected specifically to handle that type of query.
9. Output
Based on the query and data, the LLM generates a response. This can be a summary of medical info, a list of potential health risks, a draft report, or a recommendation for a clinical evaluation.
10. Telemedicine app
Definitely, telemedicine apps are an indispensable part of integrating AI in telemedicine. The validated output is presented to users through the telemedicine app, which acts as the central hub for patient data, analysis, and insights. The user-friendly format empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions.
11. Feedback loop
User feedback on the LLM’s output is a crucial part of AI in telemedicine. This helps to continuously improve the model’s accuracy and relevance.
12. Agent
AI agents play a key role by tackling complex problems and adapting to their environment. They achieve this through advanced reasoning, strategic tool use, and by leveraging memory and self-reflection.
13. LLM cache
LLM cache is also essential in using AI in telemedicine. Tools like Redis, SQLite, or GPTCache can be used to cache frequently accessed information; thereby speeding up the AI system’s response time.
14. Logging/LLMOps
Throughout the process, LLMOps tools like Weights & Biases, MLflow, and Helicone log actions and monitor performance. This ensures the LLMs are working optimally and improving over time through feedback loops.
15. Validation
A validation layer ensures the LLM’s output is accurate and reliable. You can use tools like Guardrails, Rebuff, and Guidance.
16. LLM APIs and hosting
To run telemedicine tasks and host the application when adopting AI in telemedicine, developers choose between LLM APIs and hosting platforms. API options include commercial models from OpenAI and Anthropic or open-source alternatives. Hosting can be done on major cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure, or on specialized platforms like Databricks and Anyscale. This choice is always based on the project’s specific needs.
III. What are the benefits of AI in telehealth?
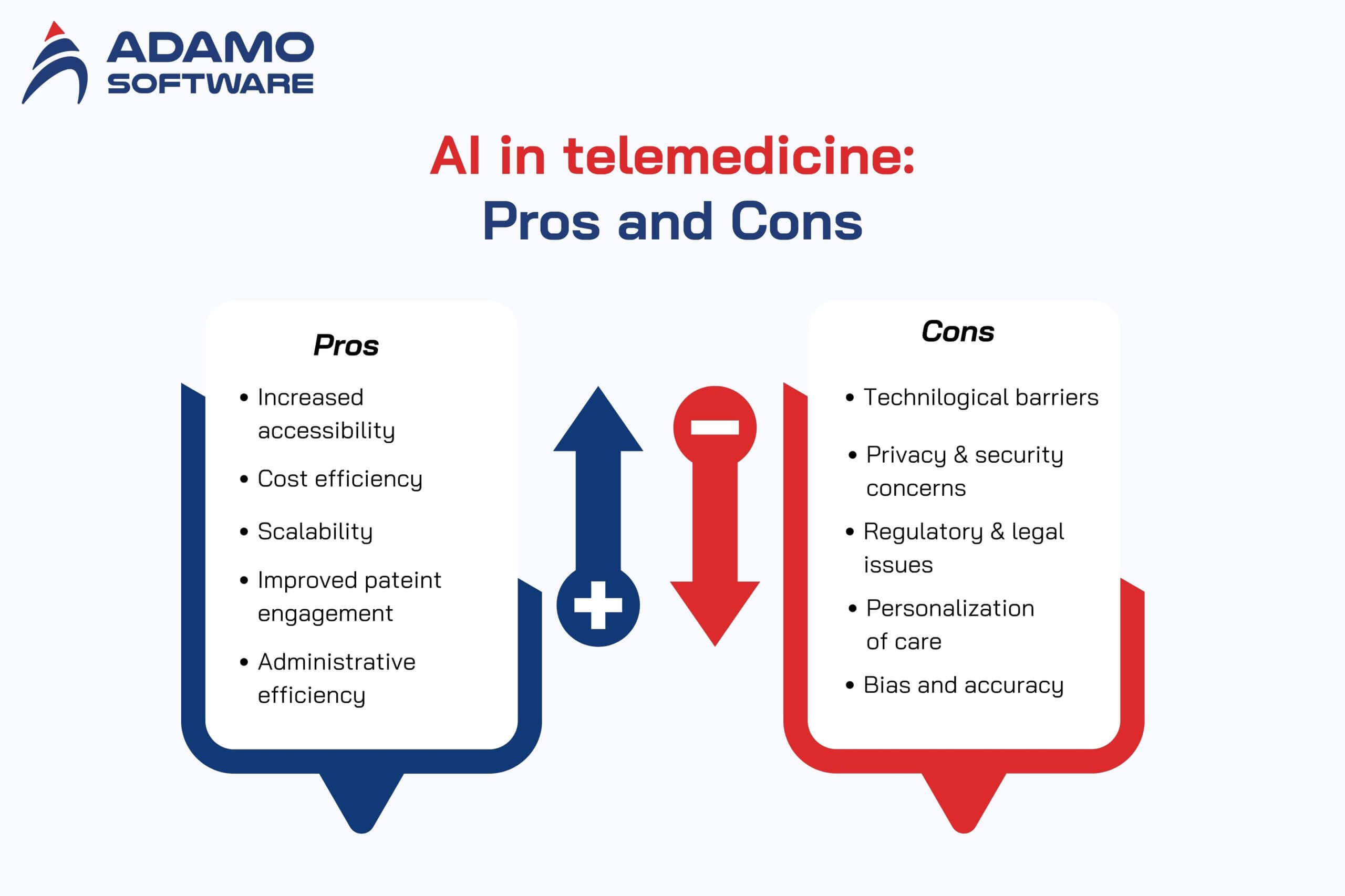
Integrating AI in telemedicine offers many benefits that improve healthcare delivery. AI is transforming telehealth by streamlining processes and providing critical insights, making healthcare more effective, accessible, and patient-focused. Below are some outstanding benefits of AI in telemedicine.
- Increased Accessibility: breaking down geographical barriers
- Cost efficiency: saving cost and improving service delivery
- Scalability: scaling telehealth with AI
- Improved patient engagement and satisfaction: enhancing telehealth experience with AI
- Administrative efficiency: reducing administrative burdens
Let’s delve into each benefit with Adamo Software!
1. Increased accessibility
AI-powered telehealth breaks down geographical barriers, providing effective healthcare to patients no matter their location. For people in remote areas, this means access to specialists and advanced care they might not otherwise have.
2. Cost efficiency
Cost efficiency is also a significant benefit of adopting AI in telemedicine. AI helps cut healthcare costs by automating routine tasks, optimizing resources, and reducing the need for expensive and time-consuming in-person visits. By handling digital assessments and follow-up care, AI enables healthcare systems to more effectively allocate human resources, saving costs and enhancing service delivery.
3. Scalability
By incorporating AI in telemedicine, you can make telehealth services more scalable, as AI systems can handle huge amounts of data and interactions at the same time. This is especially important as the global demand for healthcare grows. AI can manage many patients at once, offering personalized advice and monitoring while maintaining high standards of care.
4. Improved patient engagement and satisfaction
Improved patient engagement and satisfaction is also a superior benefit of using AI in telemedicine. AI improves the telehealth experience by using smart algorithms to provide timely, personalized interactions. For example, AI can send patients medication reminders, track their progress, and deliver customized health tips. When patients are engaged and satisfied, they’re more likely to follow their treatment plans and have better health outcomes.
You can explore more about How can AI be used in healthcare: From smarter diagnoses to safer treatments here.
Ready to Outsource?
Get top-tier IT talent without the hassle. Contact us now!
5. Administrative efficiency
Beyond clinical uses, when you adopt AI in telemedicine, you can greatly improve administrative efficiency. AI handles tasks like scheduling, registration, and billing automatically. This reduces administrative burdens and makes the entire healthcare delivery process more efficient.
IV. Challenges and ethical issues in AI-powered Telemedicine
Despite the significant benefits of online doctor consultations, several challenges and ethical considerations must be addressed to ensure their effective and equitable implementation. Below are some notable ones.
- Technological barriers: Access to reliable internet and digital skills vary widely
- Privacy and security concerns: protecting data and regulation compliance
- Regulatory and legal issues: challenges with complex regulations, licensing, and reimbursement policies
- Personalization of care: Personalized care is limited
- Bias and accuracy: AI technology is prone to bias
Let’s discuss more details about each challenge with Adamo Software!
1. Technological barriers
The Internet and technology are two main challenges of using AI in telemedicine. Not everyone has reliable internet access or is familiar with using digital tools. This makes it a difficulty to ensure that every patient has access to and can use online consultations. It also reduces the effectiveness of AI implementation in healthcare and can lead to a digital divide between population groups. Thus, it is essential to expand internet infrastructure, ensuring that everyone can take advantage of the benefits of AI in telemedicine.
2. Privacy and security concerns
When you adopt AI in telemedicine, you should also concentrate on privacy and security concerns. If the patient data is not secured, it can be leaked and used for illegal purposes. Protecting patient data is crucial during online consultations. Healthcare providers must use secure, encrypted platforms that comply with regulations like HIPAA to protect patient information.
3. Regulatory and legal issues
AI in telemedicine faces complex regulatory hurdles, including licensing regulations, data privacy, and health insurance reimbursement policies. Regional and national differences make uniform implementation difficult, especially in cross-border services. The solution is to build a unified, transparent and timely updated legal framework, and coordinate between regulatory agencies, service providers and health insurers to ensure that AI in telemedicine is deployed safely, legally and effectively.
4. Personalization of care
The ability to personalize healthcare in AI in telemedicine is still limited due to incomplete, asynchronous, and lack of diversity in medical data. It can be challenging to maintain high-quality, personalized patient care on digital platforms. To overcome this, it is necessary to expand data collection and integration from multiple sources, apply advanced machine learning algorithms and ensure information security.
5. Bias and accuracy
AI and other telehealth technologies can create biases if not properly designed and monitored. This can negatively impact the quality of care and increase health inequalities. Thus, it is essential that algorithms are accurate and equitable to prevent disparities in healthcare delivery.
V. Uses cases of AI in Telehealth
AI in telemedicine is opening up many practical applications to improve the efficiency and quality of healthcare. Here are some typical use cases showing how AI supports telemedicine in diagnosing, treating and managing patients.
- Virtual Health Assistants: delivering more accessible and intuitive healthcare
- Predictive Analytics: better managing diseases
- Automated Image Analysis: interpreting medical images
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): understanding and addressing patient queries
- Remote Patient Monitoring: facilitating immediate intervention
Let’s delve into each use case with Adamo Software!
1. Virtual Health Assistants
AI in telemedicine can be used as a virtual health assistant. AI virtual assistants, or chatbots, are vital tools for boosting patient engagement and care delivery efficiency. These assistants can provide health information, send medication reminders, and even book appointments, making healthcare more accessible and user-friendly.
2. Predictive Analytics
AI’s predictive analytics can dramatically improve patient care and health outcomes. By analyzing patient data to identify potential health risks, these models allow providers to proactively address issues before they escalate. This approach leads to better disease management and fewer hospitalizations.
3. Automated Image Analysis
By using AI in telemedicine, you can leverage AI algorithms to interpret medical images like MRIs and X-rays. This accelerates diagnostic processes and boosts their accuracy, which is especially helpful in areas that lack specialist doctors or radiologists.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP (Natural Language Processing) in AI telemedicine helps understand patient queries, providing instant and accurate responses. Furthermore, it digitizes clinical notes, which reduces the administrative workload on healthcare providers and enhances the usability of clinical data.
5. Remote Patient Monitoring
AI in telemedicine can also be used for remote patient monitoring, especially for chronic disease management. AI algorithms analyze real-time data to alert providers of critical changes, enabling immediate intervention.
VI. Final thoughts

In general, AI in telemedicine is not only a trend but also a breakthrough in enhancing treatment quality, accessibility, and healthcare service’ personalization. However, to fully exploit this potential, healthcare organizations need to have a clear strategy for integrating AI, while ensuring legal, security and user experience factors.
As one of Vietnam’s leading healthcare software development companies, Adamo Software can accompany you in this process. We can support you from integrating AI into existing software to building a completely new healthcare solution with full AI-enabled features. If you want to have more detailed information about AI-driven Software Solutions or cooperate with Adamo Software, don’t hesitate to contact our team.





